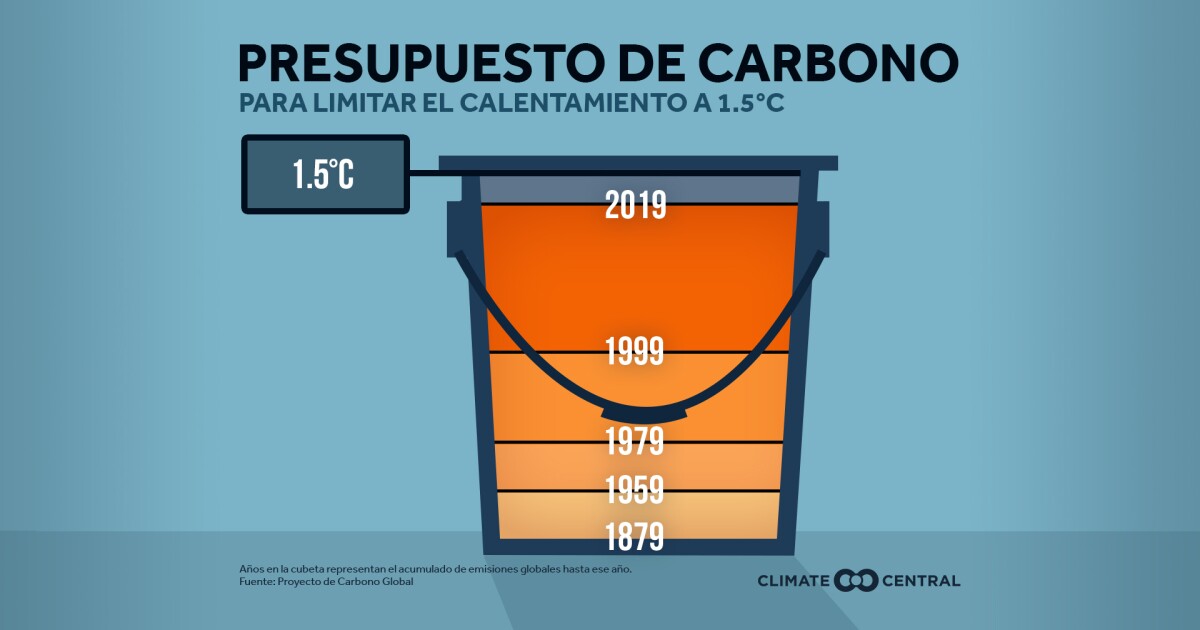
For this 2021 and the following decades, the planet needs to go on a carbon diet. Our current catastrophes – wildfires, stronger hurricanes, and rising seas – are consistent with the warnings scientists made in the 1980s and 1990s.
The past burning of fossil fuels, including oil, coal and natural gas, has released greenhouse gases into the atmosphere and made the earth be hot by 2 ° Fahrenheit (a little over 1 ° Celsius) since the pre-industrial era (1880-1900).
The term “net zero emissions” means that the greenhouse gas emissions released are balanced by an amount equal to that removed from the atmosphere.
In 2015, Paris Climate Agreement set goals for countries to try to limit the increase in global warming to well below 2.0 ° C (3.6 ° F) above pre-industrial levels to prevent the impacts of climate change from worsening, and redouble efforts to limit the increase temperature below 1.5 ° C (2.7 ° F). According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), for reach These targets, global greenhouse gas emissions must be cut in half by 2030 and reach “net zero emissions” by mid-century for the 1.5 ° C target.
For this 2021 and the following decades, the planet needs to go on a carbon diet.
(Climate Central)
–
–
This requires not only drastically reducing our greenhouse gas emissions rapidly, but also removing CO2 from the atmosphere.
Scientists, engineers and other researchers are exploring pathways and models to understand what must happen in the next few decades for the United States to reach net zero emissions. There are several initiatives to achieve zero emissions such as Net Zero Emissions America Project (NZAP), models various technological pathways to achieve net zero greenhouse gas emissions by mid-century. While their models and projections may incorporate different technologies and have different results, the projects highlight the same core areas of the economy that need to undergo significant transformation to reach net zero emissions:
- Carbon-free electricity creation
- Electrification of transport
- Adopt energy efficiency measures and electrify our buildings
- Industry and manufacturing decarbonization
- Transform our agricultural and food habits
Most of the ways to keep global temperatures in check, and all roads to stop at 1.5 degrees, incorporate the absorption of carbon emissions from the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide is the only greenhouse gas that can be removed from the atmosphere and stored; but doing it on a scale large enough to make a difference is challenging.
–