The definition of isotopes and examples are one of the materials that must be studied. Isotopes are one of the structures in atoms. Even matter about isotopes is part of nuclear chemistry.
Also Read: What are the uses of haloalkanes, their types, and properties?
Completely Peel Isotope Definition and Examples
Isotopes are elements that are twins, but not identical. This atomic structure actually has the same atomic number, but a different mass number.
The name isotope itself comes from the Greek “isos” which has the same meaning. Then “topos” which means four.
So, an isotope is an element with an atomic number and occupy the same place on the periodic table.
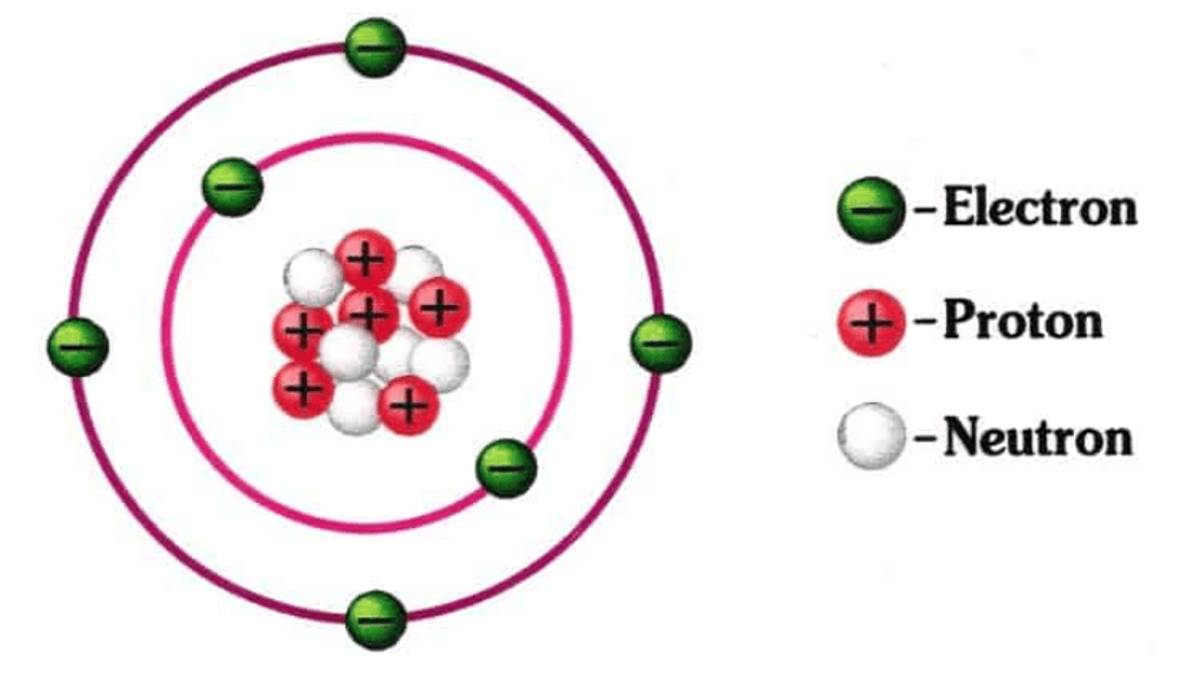
In other words, isotopes have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. For example 2412Mg with 2512Mg and 2612Mg.
Investigations with mass spectrographs show that almost all elements exist in some mixture of isotopes.
Every element in the periodic table must have at least one or more isotopes. For example, hydrogen has three isotopes, namely protium, tritium, and deuterium.
All three hydrogen isotopes have one electron and one proton in common, so the atomic number is the same.
Protium has no neutrons. While deuterium has one neutron and tritium has two neutrons. It is this difference in neutrons that keeps the mass numbers of the three isotopes different.
Also Read: Understanding Electron Configuration: Basic Rules and Theory
Isotope Stability
After knowing the definition and examples of isotopes, you must also master the stability of isotopes.
An isotope can be said to be stable if it does not show a tendency to change spontaneously without a trigger.
Of course, the stability of each isotope is different. That’s because it depends on the number of neutrons and protons.
The ratio of the ratio of the number of neutrons and protons in the atomic nucleus greatly affects the stability of an isotope. Neutrons and protons in an atom must have the same number or ratio of 1:1.
If the ratio is the same, then it becomes a stable isotope marker. On the other hand, if the ratio is outside 1:1, it is a sign that the isotope is unstable.
Deuterium is an example of a stable isotope of hydrogen. That’s because deuterium has one neutron and one proton which makes it in the stable isotope band.
On the other hand, Hgg has 120 neutrons with 80 protons. Thus, the ratio of Hg is 1.5.
Also Read: History of the Discovery of Electrons, Negatively Charged Subatomic Particles
That makes Hg unstable and is above the isotope stability band. Apart from being in and above the isotope stability band, there are also several elements below it.
Some examples of elements that fall under the equilibrium band are Be. In Be there are 3 neutrons and 4 protons. Because of the ratio of protons and neutrons, the element Be becomes 0.75.
Mastering the definition and examples of isotopes is very important because it is the main material in chemistry and one that gets the predicate is quite difficult. (R10/HR-Online)
–