[이데일리 이승현 기자] Although the deposit rate at US banks was virtually close to zero, the balance of deposits appeared to be increasing. It is interpreted as’preliminary savings’ in preparation for future uncertainty.
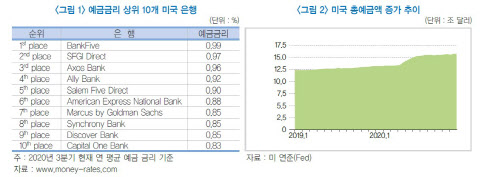
According to the Korea Financial Research Institute’s report on the increase in deposits and implications in the environment of low interest rates in the United States on the 19th, the average annual deposit interest rate of commercial banks in the United States in the third quarter of this year was 0.192%, down 0.082% points from the previous year. The current highest deposit rate is also below 1% per year.
Large banks with large deposits, such as JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America, are aggressively cutting deposit rates. Small and medium-sized banks focusing on online are also joining the cut line, the report said.
However, rather than withdrawal, the inflow of funds continues. US commercial banks’ total deposits amounted to $1.5 trillion as of the end of October, an increase of about 20% from $1.3 trillion in January.
In particular, deposit growth is led by small customers with a balance of less than $2,500 at the beginning, and gradually spreads to large customers with a balance of more than $5,000. The average monthly increase rate of large deposits from June to October was 8%, far exceeding the growth rate of small deposits (2%).
The report evaluated that the increase in small and large deposits is an aspect of expanding preliminary savings as a safety net for future uncertainty situations for both households and businesses. He pointed out that this implies that there is a growing need for the Biden US administration, which will be launched in January next year, to implement more intensive additional economic stimulus measures.
For the banking sector, the report ordered that the business model should be continuously improved or optimized in the direction of improving the efficiency of financing and productivity of fund management.
|
– .