Quoted from the Forbes page, Wednesday (20/4/2022), the researchers made a small lens arrangement on metalenses cameras that were specifically designed to manipulate light in a certain way. Like the crystal structure of the trilobite lens, the researchers designed the metalens made of millions of tiny rectangular nanometer-scale titanium-oxide pillars.
The shape and orientation of the nanopillars focus light in such a way that they simultaneously act as a macro lens (for close objects) and telephoto lenses (for distant objects). Special software is used to produce the final image and correct defects such as blurring and color aberrations.
Read also; Cannibalism Has Been Happening Since the Age of Dinosaurs, Revealed in Trilobite Fossil
Metalenses and software can be used to develop new high-tech camera systems. Such a large and light depth of field camera promises to revolutionize future high-resolution imaging systems.
In particular, the camera will greatly increase the capacity to produce highly detailed landscape images and to capture single-shot objects of various colors, shapes and sizes in one shot. A mini camera featuring a bifocal lens with a record-breaking depth of field, the distance at which the camera can produce sharp images in a single photo.
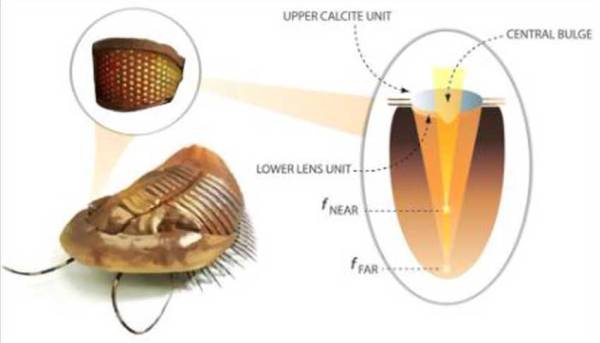
NIST researchers Amit Agrawal and Henri Lezec of the University of Maryland at College Park and Nanjing University, created the metalense camera inspired by the eye of Dalmanitina socialis, a trilobite group of extinct marine arthropods that has ruled the oceans for more than 270 million years.
Read also; Shining eyes, the animal that shocked Depok is believed to be a weasel
Trilobites have a wide range of vision thanks to compound eyes, single eyes made up of tens to thousands of small, independent units, each with its own cornea, lens, and light-sensitive cells. One group, the Dalmanitina socialists, was very far-sighted.
 –
–
The bifocal eyes of Dalmanitina socialis, each mounted on a stalk and consisting of two calcite lenses that bend light at different angles. This allows these sea creatures to simultaneously see prey floating nearby as well as distant enemies approaching from afar.
(Web)
–

