Author: Chen Huafu
Sleep is very important to human health, but it is difficult to understand. The Internet media is full of many articles on how to sleep, but most of them are one-sided and contradictory. Even hospital doctors have difficulty in treating various insomnia and sleep deprivation. health problems. This article systematically and clearly provides sleep knowledge to help everyone sleep well.
1) Human circadian rhythmbiological clockAffects sleep:
It wasn’t until the Nobel Prize in 2017 that humans understood the structure of the human bodycircadian rhythmscientists studied fruit flies, which have a very similar genetic makeup to humans, and they isolated a species that helps control the human bodybiological clockgene that produces a protein that accumulates in cells at night and then breaks down during the day. This process affects how long you sleep, how sharp your brain functions, and more.
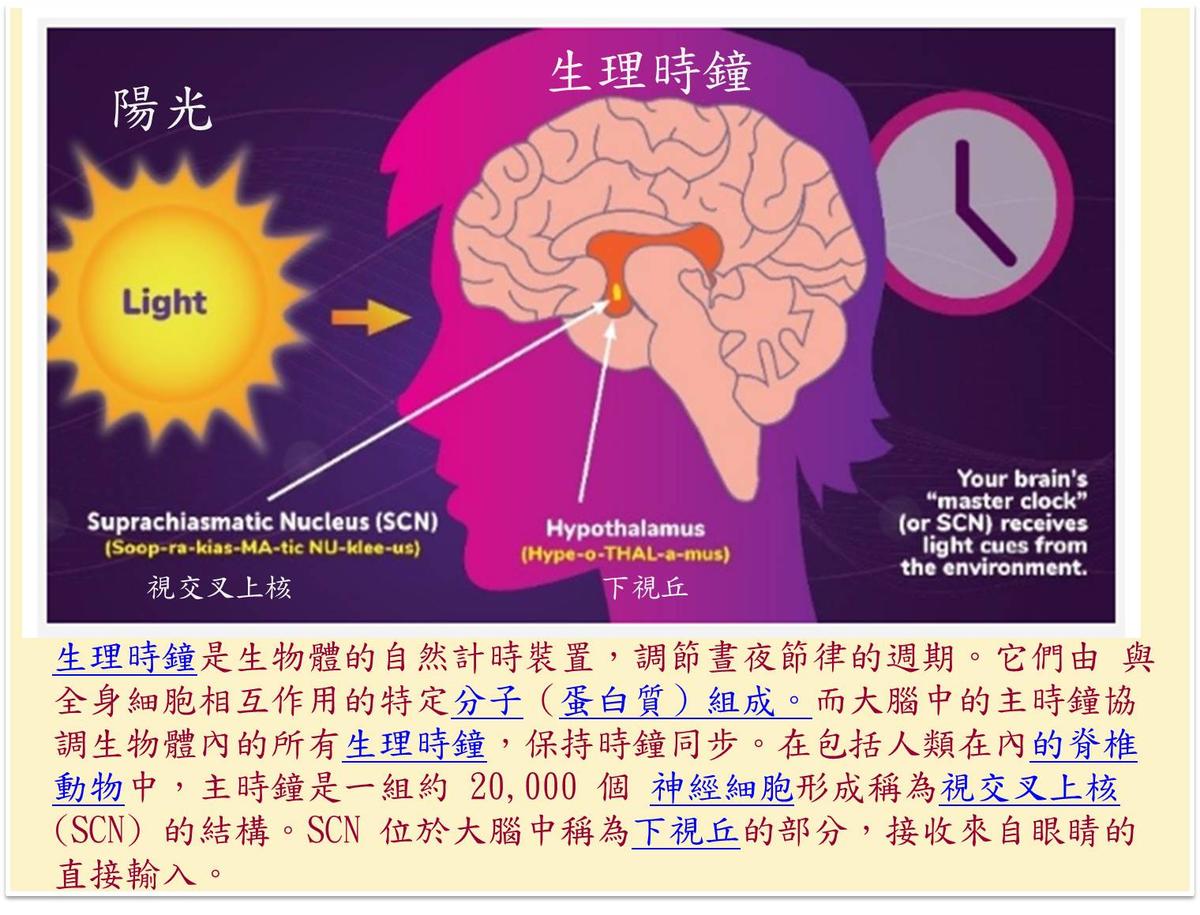
biological clockIt is the organism’s natural timing device that regulates the circadian rhythm cycle.They are composed of specific cells that interact with cells throughout the bodymolecular(protein) composition.almost every organizeand organAll contain biological clocks.Researchers have made clock molecules in humans, fruit flies, mice, plants, fungi and several others componentSimilar ones have been found in organisms Gene.The master clock in the brain coordinates all activities in the organismbiological clock, to keep the clocks synchronized.including humansvertebratesthe master clock is a set of approximately 20,000 nerve cellsformed is calledsuprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) structure. The SCN is located in a part of the brain called the hypothalamus and receives direct input from the eyes.
(Picture information:circadian rhythm)
suprachiasmatic nucleusControls the production of melatonin, a hormone that makes people sleepy. It receives information about incoming light from the optic nerve, which carries information from the eye to the brain. When there is less light (such as at night),suprachiasmatic nucleustells the brain to produce moremelatoninwhich will make you drowsy.
2) Melatonin and sleep:
melatoninAffected by light and sunlight patterns, during the day or when there is sufficient light,melatoninThe amount of secretion will decrease; usually the secretion is strongest from 11 o’clock in the middle of the night to the early morning of the next day.Therefore, it is best to bask in the sun between 7 and 9 in the morning. After 14 to 16 hours in the sun, the brain’spineal glandbegins to secretemelatonin. Turn off the lights at 11pm and sleep in the dark.
pineal glandThe secretion of the body is very regular. Once you stay up late, the next daymelatoninThe amount of secretion will decrease, and it will take about 11 days to return to normal. Therefore, the human body often suffers from insomnia, sleepiness during the day, and yawning during this period.
Middle-aged and elderly peoplemelatoninThe amount of secretion will also gradually decrease with age, leading to difficulty in falling asleep andjet lagDifficult to adjust.
Matthew.WalkerThe professor thinksmelatoninIt is not a powerful sleep aid in itself and has obvious effects on sleep.placebo effectshould not be underestimated, he said: “Once the sleep process starts, the concentration of melatonin will slowly decrease from night to early morning. At dawn, sunlight enters the brain through the eyes (even if the eyes are closed), stepping on the pineal gland. The brakes are applied, stopping the release of melatonin. Now there is no more melatonin circulating in the blood, which tells the brain and body that the sleep finish line has been reached.” (“Why sleep? : The new science of sleeping to improve health and learning ability, and dreaming to be creative》Matthew. Walker, p. 23, hereafter referred to as “for”)
3) How much sleep do humans need and how much sleep do they need?sleep quality:
The recommended sleep hours by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine are as follows:
(Image source: American Academy of Sleep Medicine)
Sleep quality is not the same as sleep quantity. Sleep quantity measures how long you sleep each night, while sleep quality measures the quality of your sleep. According to the National Sleep Foundation, good sleep quality must meet the following four points:
(Image source: American Academy of Sleep Medicine)
4) Humans need to take a nap, but taking a nap for too long increases melatonin secretion, which affects sleep at night:
Matthew.WalkerThe professor believes that humans need a nap. He said: “The true two-stage sleep pattern is a continuous long night sleep plus a short nap. There is evidence from anthropology, biology and genetics. Measurable in all humans so far.” And the tragic consequences of canceling the nap habit
: “A group of researchers at the Harvard School of Public Health decided to quantify the health effects of this drastic change. They surveyed more than 23,000 Greek adults, both men and women, ranging in age from 20 to 8 years old. Age 13. The researchers followed for six years, focusing on cardiovascular changes during which many people ended their nap routine. The results, like those of countless Greek tragedies, are heartbreaking, and in this case literally mean , in the most severe way. At the beginning of the study, these people had no history of heart disease or stroke, and therefore no cardiovascular disease problems. However, in those who gave up their regular naps, compared with those who maintained their regular naps , during this six-year period, the risk of death from heart disease increased by 37%. This was particularly serious among workers, with a lack of naps increasing the risk of death by more than 60%.” (“We”, page 75)
But taking a short nap or napping for too long will increase melatonin secretion and affect your sleep at night.
In professional sports, the difference between the gold medal and the last place is very close. Taking a nap before the game may be the key: “The 100-meter dash star “Lightning” Bolt has taken a nap before the game many times. Deeds, including hours before breaking the world record and later winning the Olympic gold medal in the final.Our research backs up his wisdom: daytime naps, in addition to conserving energy and reducing muscle fatigue, if taken in adequate amountssleep spindles, will also bring significant improvement to motor skill memory. ” (“Wei”, page 133)
(5. Washing your face before going to bed and extending your hands and feet outside the quilt at night can lower your core body temperature:
human’scircadian rhythmOfbiological clockCoordination Committeecore body temperaturereaching the lowest point around 2 o’clock in the night, and reaching the highest point between 5 and 7 o’clock in the morning.Matthew.WalkerThe professor said: “Body temperature drops near normal bedtime (as shown in the picture) and reaches its lowest point about two hours after falling asleep. However, this cyclical change in body temperature has nothing to do with whether you actually fall asleep. If you are kept up all night , your core body temperature will still follow the same pattern. Although the drop in body temperature helps initiate sleep, the body temperature itself will continue to rise and fall repeatedly over the twenty-four hour period whether you are asleep or not. This is a classic example of rhythm these days. Like a metronome, keep repeating, never making mistakes.” (“We”, page 19)
(Picture information: “Why sleep? : The new science of sleeping to improve health and learning ability, and dreaming to be creative》)
During strenuous exercise or when under excessive stresssympathetic nervous systemhyperactive,core body temperatureIf it rises, it will be difficult to fall asleep.Matthew.WalkerThe professor explained: “To initiate sleep, core body temperature needs to be lowered. For patients suffering from insomnia, their core body temperature rises due to increased metabolic rate, and their brain temperature is also higher, making it more difficult to initiate sleep.” ( “For”, page 253)
He added: “To successfully initiate sleep, your core body temperature must drop by about one degree Celsius. Therefore, it is always easier to fall asleep in a room that is too cold than one that is too hot, because a cold room at least shifts the temperature of the brain and body in a direction suitable for sleep. Pull.” (“Wei”, page 283)
Washing your face before going to bed and stretching your hands and feet out of the quilt at night can reducecore body temperature。Matthew.Walker“Heat dissipation from the extremities may also explain why we sometimes stick our hands or feet out from under our quilts at night,” the professor explains. “That’s because our core body temperature becomes too high, although we don’t usually realize it. If you have children , when you check how they slept late at night, you may see the same phenomenon: their hands and feet are hanging on the edge of the bed in a very cute posture, completely different from the way you covered their hands and feet with a quilt when they first fell asleep. Disobedient The hands and feet will help cool the core of the body, while also helping to fall asleep and stay asleep” (“Wei”, page 284)
(8 owlof people who are chronically sleep deprived:
adultWork and rest pattern(chronotype) is a morning person orowl, is largely determined by genetics.What if you areowlchances are one or even both of your parents areowl。Matthew.WalkerThe professor said: “Night owls have to go to sleep very late at night, but they have to get up at the same time as the early birds. As a result, they are deprived of sleep for a long time and become a veritable candle burning at both ends. Then, health problems caused by lack of sleep will befall night owls. This includes higher rates of depression, anxiety, diabetes, cancer, heart attacks, and strokes.” (Wei, page 21) Therefore,owlYou should also abide by the “Twelve Rules of Healthy Sleep” mentioned below to get enough sleep.
(9 Sleep problems in middle age and old age:
Matthew.WalkerThe professor said: “As we grow older, sleep begins to become more problematic. Older adults often have a number of health conditions, and the effects of medications they take more frequently make it more difficult for older adults on average. Reaching the same amount of sleep as young people, the degree of fatigue recovery through sleep is not as good as that of young people. Some people think that older people have less sleep needs, which is a complete myth. The sleep needs of older people should be the same as in middle age. Pretty much, it’s just harder to get the same amount of sleep. One piece of supporting evidence: some large surveys have shown that even though older people actually sleep less, they still need more sleep and actually try to sleep as well as younger people. There are as many people as there are people.” (“Wei”, page 99)
He added: “There is a more immediate and equally dangerous effect of fragmented sleep in the elderly that is worth mentioning here: falls and fractures caused by nocturnal trips to the toilet. When we wake up at night, we are often still confused. In addition to unclear cognition, the environment is also darker. Also, since you were originally lying on the bed, when you stand up and start moving, the blood will be pulled from the head to the feet due to gravity, resulting in dizziness and Unsteady walking. This is especially true for older adults, who often have problems controlling their blood pressure. All of this suggests that older adults are at higher risk of tripping, falling, and breaking bones when going to the bathroom at night.” (We, Page 101)
Therefore, the elderly should abide by the “Twelve Rules of Healthy Sleep” mentioned below to get enough sleep.
10) Twelve rules for healthy sleep:
Matthew.WalkerProfessor in his book “Why sleep? : The new science of sleeping to improve health and learning ability, and dreaming to be creative“The appendix provides “Twelve Rules for Healthy Sleep”, which I briefly describe as follows:
(1) Observe regular sleep time. Go to bed at the same time and wake up at the same time every day.
(2) There are many benefits of exercise, but you should not exercise too late. Try to exercise for at least thirty minutes every day, but end it two to three hours before bed.
(3) Stay away from caffeine and nicotine. Caffeine is a stimulant found in coffee, cola, some teas and chocolate, and its effects can take eight hours to wear off, so a cup of coffee in the evening can keep you awake at night. Nicotine is also a stimulant, which often causes smokers to sleep lightly. Additionally, smokers often wake up too early in the morning when quitting nicotine.
(4.) Avoid drinking alcohol before going to bed. A drink before bed may help you relax, but drinking too much can cause you to miss REM sleep and make you sleep shallower. Heavy drinking may also cause breathing problems at night. When the effects of alcohol are gradually consumed in the body, it will be easier for you to wake up in the middle of the night.
(5) Avoid eating big meals too late and drinking too many drinks. Causes indigestion, nocturia, and disturbs sleep.
(6) Ask your doctor whether the medicine you are taking interferes with sleep and whether it can be taken earlier in the day or night.
(7) Don’t take a nap after three o’clock in the afternoon. May make it harder to fall asleep at night.
(8) Relax before going to bed.
(9) Take a hot bath before going to bed. After taking a bath, your body temperature will drop, making it easier to fall asleep.
(10) The bedroom should be dark and slightly cool. TV, mobile phone or computer will interfere with your sleep.
(11) Get some sun exposure. Daylight is key to regulating your daily sleep routine. Try to spend at least thirty minutes outside in the sun every day. And dim indoor lights before going to bed.
(12) Do not lie in bed while awake. If you’re still awake twenty minutes after going to bed, or if you start to feel worried or anxious, it’s a good idea to get up and do some relaxing activities until sleepiness sets in.Anxiety about not being able to fall asleep can make it harder to fall asleep
in conclusion:
Sleep is very important to human health but difficult to understand. This article systematically and clearly provides the scientific knowledge of sleep that the public should know, as well as the twelve rules of healthy sleep, so as to help everyone sleep well.
Please read the “Chen Huafu Column” series of articles on the essence of learning:
(
The theory of “Thinking is a conscious series of memories” started a revolution in the history of thought – the nature of learning (1)
What is “thinking”? How to gain “insight”? What is a “thinker”? ─The nature of learning (2)
What is “memory”? How to “memory”? The nature of “memory”? ─The nature of learning (3)
The truth and reflection on learning – the nature of learning (4)
“Almsgiving” is the “modern enlightenment” of life – the essence of learning (5)
Talking about “fear” – the nature of learning (6)
Explore the “guilt” of Chinese people? ─The nature of learning (7)
Are you lonely? ─The nature of learning (8)
How does the human brain think innovatively? ─The nature of learning (9)
The essence and meaning of “modern enlightenment” – the nature of learning (10)
Are you “modern-day enlightened”? ─The nature of learning (11)
“Reinforcement learning” of artificial intelligence and the pros and cons of human learning – the nature of learning (12)
Gamma Waves (40 Hz), Memory, Dementia, and Music Therapy (2023 Edition) – The Nature of Learning (13)
Reflecting on the truth about physical science education – the nature of learning (14)
What makes quasi-intelligence really better than AI computer Go? ─The nature of learning (15)
Describe in detail my 40-year learning journey – the nature of learning (16)
AI helps people improve their memory and thinking abilities – suitable for young and elderly people – the nature of learning (17)
AI completely changes the face of university science and engineering education – the nature of learning (18)
Can AI simulate human learning really be more innovative than humans? ─The nature of learning (19)
Is there really any difference between AI deep learning and the study of “I Ching”? ─The nature of learning (20)
Appreciation of the painting aesthetic ability of AI ChatGPT─The essence of learning (21)
Please understand the nature of intelligence: How far behind humans is GTP4’s “Artificial General Intelligence” (AGI)? ─The nature of learning (22)
The significance of Taiwan Xu Haohong’s Go Asian Games gold medal in learning Go – the essence of learning (23)
On Talent, Luck, and Success – The Nature of Learning (24)
What you should know about the science of sleep – the nature of learning (25)
)
2023-11-12 02:25:32
#science #sleep #nature #learning #Square #Vocus