Summary of judgment Constrution DRM inc. C. Kalad’art Buildings Inc
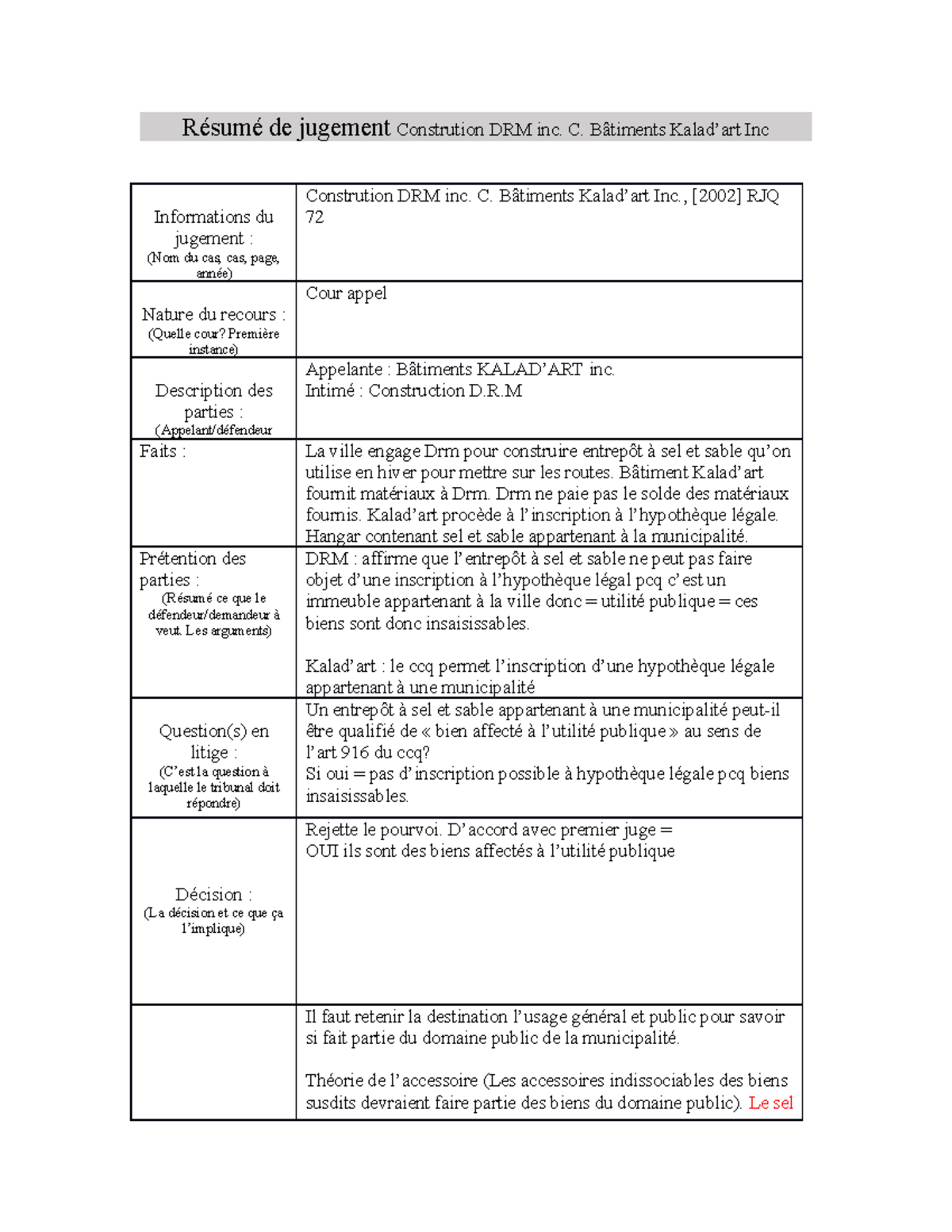
Judgment information: (Case name, case, page, year)
Constrution DRM inc. C. Bâtiments Kalad’art Inc., [2002] RJQ 72
Nature of the appeal: (Which court? First instance)
Court appeal
Description of the parties: (Appellant / defendant
Appellant: KALAD’ART Buildings inc. Respondent: Construction DRM
Facts: The city hires Drm to build a salt and sand warehouse which is used in winter to put on the roads. Kalad’art building supplies materials to Drm. Drm does not pay the balance of materials
provided. Kalad’art proceeds to register for the legal mortgage.
Hangar containing salt and sand belonging to the municipality. Contention of the parties: (Summary of what the defendant / plaintiff wants. The arguments)
DRM: affirms that the salt and sand warehouse cannot be subject to registration for the legal mortgage pcq it is a building belonging to the city therefore = public utility = these goods are therefore elusive.
Kalad’art: the ccq allows the registration of a legal mortgage belonging to a municipality
Question (s) in dispute: (This is the question the court must answer)
Can a salt and sand warehouse belonging to a municipality be qualified as “property assigned to the public utility” within the meaning of art 916 of the ccq? If yes = no registration possible for legal mortgage pcq elusive goods.
Decision: (The decision and what it involves)
Dismisses the appeal. Agree with first judge = YES they are goods allocated to the public utility
It is necessary to retain the destination general and public use to know if it is part of the public domain of the municipality.
Accessory theory (The accessories inseparable from the aforementioned goods should be part of the goods in the public domain). Salt
Reasons: (Reasons for making this decision)
in this case which is of public utility and as it must be in a building, therefore the building therefore becomes a building of public utility.
The warehouse is not in itself essential to the functioning of the administration of the municipality and to the provision of services, but such a warehouse = essential to the proper functioning of a municipality, ie the maintenance of the streets. Street maintenance = essential service provided by the municipality to its citizens to ensure their safety. The public utility is indirect in this case. The second or we prove that a bin will be used for public utility = public domain. The sand is vital for the well-being of citizens, therefore since it is the accessory it can be considered as an asset allocated to the public utility.
Comments: (Imp. Notes Or Dissent Note)
Public utility for some authors = either direct or indirect (property is not used by the population but is owned by the municipality in the general interest and for a municipal purpose.
School not well of public utility pcq it’s just for children. Not for everybody.
–