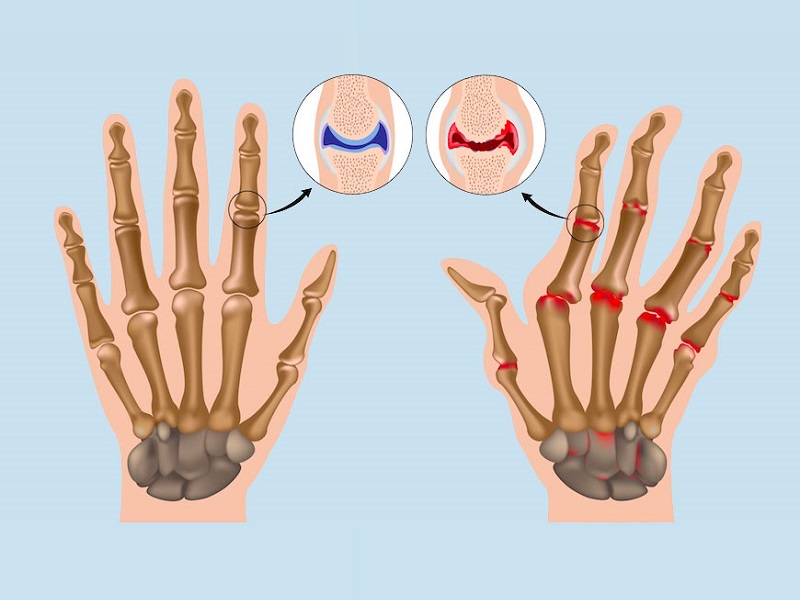
The disease, due to inflammation of the joints, occurs with pain, swelling, stiffness on movement e next one loss of functionality of the joints involved. The pain, the main symptom, is spontaneous, continuous, often difficult to quantify, present at rest and tends to improve with movement.
The rigidity joint is most intense upon awakening and can last for hours, if not the whole day. This feature differentiates rheumatoid arthritis from other joint diseases such as osteoarthritis, in which stiffness tends to fade after a few minutes.
The loss of functionality it can be caused in the initial phase by synovitis (inflammation of the synovial membrane) and in the advanced phase by joint deformities and ankylosis.
The joints commonly involved bilaterally and symmetrically (a typical feature of the disease) are the small joints of the hands and feet, wrists, elbows, shoulders, hips, knees and ankles. The onset is extremely variable.
In most cases it is treacherous and gradual (65-70%) but in some cases it is acute (10-25%). Joint symptoms can be associated with systemic symptoms such as fatigue, fever, weight loss, muscle soreness e rash cutaneo.
Diagnosis.
In the majority of cases (55-70%), the disease manifests itself gradually and insidiously, with the appearance of joint pain accompanied or not by prolonged morning stiffness, followed by the appearance of signs of joint inflammation within weeks or months. In addition, the onset symptoms are similar to the onset symptoms of various rheumatic diseases.
Because of this, especially in the early stages, it can be difficult to diagnose. The diagnostic suspicion should be placed whenever one or more joints remain swollen and painful for more than six weeks. Laboratory tests help in formulating a correct diagnosis. About 70% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis have high blood levels of Rheumatoid Factor (FR).
The marker more specific is the presence of antibodies anti-citrullinated peptides (anti-CCP). There are also other laboratory tests which, although non-specific, can be altered during the disease: the increase in VES and C reactive Protein (PCR) (suggestive of an ongoing inflammatory process), decreased hemoglobin (anemia).
Among the instrumental examinations, the first investigation to be performed is traditional radiology (X-ray hands and feet) which, however, in the initial stages is unable to highlight erosions, typical alterations of the disease.
The examination to be carried out immediately together with the radiography is theultrasound articulate which will demonstrate joint effusion and the possible presence of the synovial cloth. Another useful test for diagnostic purposes in selected cases is the magnetic resonance capable of demonstrating joint inflammation and possible inflammation of the bone (bone edema).
Treatment and medication.
The drugs currently available for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis have improved the prognosis of the disease. The therapy, if started early, shortly after the onset of the first symptoms, is able to modify the natural history of the disease and prevent irreversible joint damage.
It is therefore essential for the success of the therapy that the patient with symptoms suggestive of rheumatoid arthritis (pain and swelling of at least 3 joints for more than 6 weeks, especially in small joints of the hands and feet, and stiffness on awakening greater than 30 minutes) is promptly referred to the rheumatologist to diagnose and start therapy as early as possible.
The therapy aims to:
- Reduce the intensity of pain;
- Stop the destructive process in the joints;
- Recover function and therefore prevent the loss of working capacity.
For the first purpose, i non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Fans) ei corticosteroids.
The second purpose serves drugs that modify the course of the disease, the so-called distinct background drugs traditional background medications (in particular Methotrexate, leflunomide, salazopyrine) e biotechnological drugs, or drugs aimed at specific targets responsible for the inflammatory process, which must be used after the failure of therapy with traditional drugs.
The third purpose is joint-neuromuscular rehabilitation and possibly orthopedic surgery.
–