SEEDING TIME
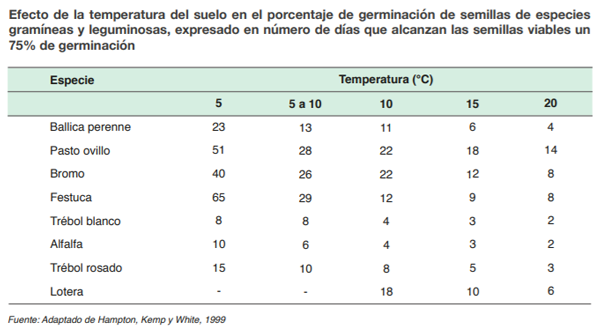
The time of sowing is defined by the temperature and humidity of the soil. Temperatures below 8 ° C are not suitable for establishing a pasture. Each species has a temperature range at which it germinates, legumes being the least demanding group.
If the soil temperature is adequate for the species, humidity becomes the determining factor. The highest percentage of germination and seedling emergence is recorded when the soil is at field capacity, that is, at the moment where the soil is wet and does not have the capacity to retain more water. This moment is established between the point of field capacity and the point of permanent wilting, the moment where the seeds achieve their maximum germination and the plants present the highest production capacity.
There are two traditional periods of establishment of pastures and supplementary crops: February – April and August – October, however, given the conditions of humidity and soil temperature, the sowing period can be extended even further, reaching almost nine months of the year. .
FERTILIZATION
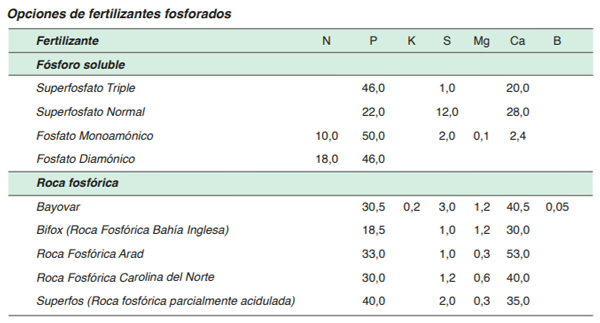
The application of fertilizers in the planting furrow, especially phosphorus, aims to increase the possibility that the seedlings have access to this nutrient once their root system is formed and functioning. Fertilizers containing phosphorus are of low solubility and therefore not very mobile in the soil profile, a situation that indicates that their efficiency is directly related to the proximity that this element has with the root system of plants, which is why, in Broadcast planting, a level of phosphorus in the soil above 30 mg / kg is required. In line sowing, the efficiency of utilization of this element rises by at least 300%, since the fertilizer remains close to the area where the entire rhizospheric environment of the established plants will develop.
Phosphate rock: It corresponds to a primary product that has not been acidified like superphosphates. The acidulation and release of phosphorus to the soil solution occurs naturally when the fine product is mixed with an acidic soil or when it faces organic acids generated by the roots and that is located in the rhizospheric environment of plants, in special of legumes.
The rate of solubilization of phosphorus is related to the acidic environment and precipitation. This product has a very slow solubility in soils with a pH greater than six and in areas where the annual precipitation is less than 800 mm.
If phosphoric rocks are used in the establishment of pastures, it should be considered that the product should be incorporated into the soil at least one month before sowing and the dose of phosphorus doubled or tripled so that the plants can have access to phosphorus and do not present deficiencies in its early stages of development. To avoid the initial deficiency, it is feasible to include a phosphor choke in the sowing machine that will go to the sowing furrow.
By applying high doses of phosphate rock to the sowing, this is two or three times that required by an acidulated phosphor (superphosphate), it is feasible to eliminate or reduce the maintenance dose in the following two years.
On the other hand, the application of calcareous amendments is contrasted with the use of phosphoric rocks. The rocks require acid pH, therefore the correction of this parameter through amendments generates a reduction in the solubilization rate of the phosphate rock.
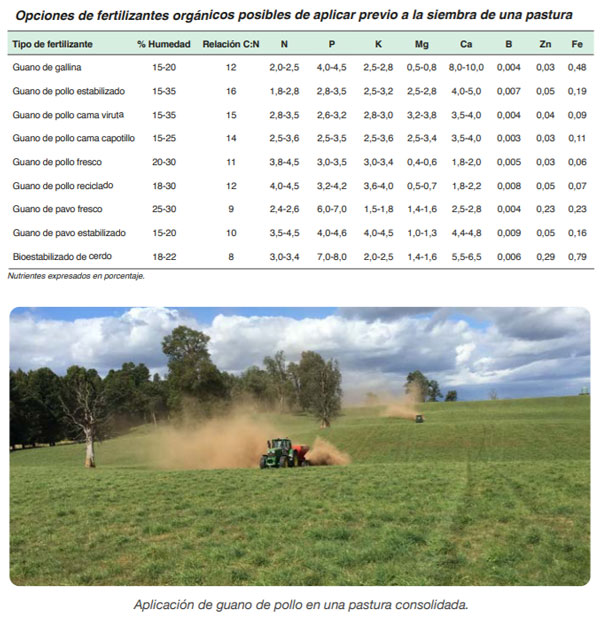
Organic fertilization: Great benefits have the use of organic fertilizers in the establishment of pastures. Contribution of nutrients of high biological value, increased biological activity of the soil, increased water retention capacity of the soils and development of high bromatological quality pastures, are some of the virtues of the use of this type of fertilizers .
This product that quickly delivers nutrients such as nitrogen, potassium and sulfur to the soil solution, favors the development of weeds that will compete with the emerged plants. This problem that can even generate the loss of pasture, it is feasible to face it in two ways. The first is to apply and incorporate the organic fertilizer 45 days prior to sowing, wait for the emergence of the weeds and apply a chemical fallow, which will reduce the weed load in the first stages of pasture development. The second option is to sow with a phosphorous choke and apply organic fertilization after the first grazing once the pasture is consolidated.
–