One in two people will be obese in a few years. The number of overweight or obese people is constantly growing worldwide, despite widespread information about how you can have a healthy lifestyle. The World Health Organization has recognized that, in this century, obesity has an equal or higher prevalence compared to malnutrition and infectious diseases. Because, In the absence of drastic prevention and treatment measures, it is estimated that by 2025, over 50% of the world’s population will be obese.
But how is the situation in Romania?
Surgeon Mihai Ionescu, a specialist in obesity, oncology, laparoscopic surgery and pelvic floor surgery, provides statistics on the latest studies and explains how extra pounds affect people’s health.
“Obesity occurs as a result of an energy imbalance between calories consumed and calorie intake. This results in an excess of energy, which leads to excessive body weight. Overweight and obesity are defined as abnormal or excessive accumulations of fat that can affect health. Body mass index (BMI) is defined as the weight of a person in kilograms divided by the square of his height in meters (kg / m2).
For adults, the WHO defines overweight and obesity as follows:
Obesity is a chronic disease, with a very high prevalence and affecting men and women of all races and ages.
Pre-obesity and obesity are important public health issues and need a common strategy, which includes promoting healthy eating habits and a more active lifestyle, as well as appropriate treatment and care.
“In addition to causing various physical disabilities and psychological problems, being overweight dramatically increases a person’s risk of developing a number of noncommunicable diseases, including cardiovascular disease, cancer and diabetes.” says the surgeon Mihai Ionescu.
What is the situation in Romania
“The prevalence of cases of overweight in Romania exceeds the European average by a few percent. Specifically, according to statistics, 49% of women are overweight and 10% have exceeded the obesity threshold, and 63.2% of men are overweight and 10% obese.
It is also interesting to see how the percentage of obese people in our country has increased in the last 40 years.
If in 1975, only 8.3% of the population was obese, the percentages increased over the years. In 1990 it was 13%, in 2000 it was 16.2%, and in 2016 it reached 22.5%.
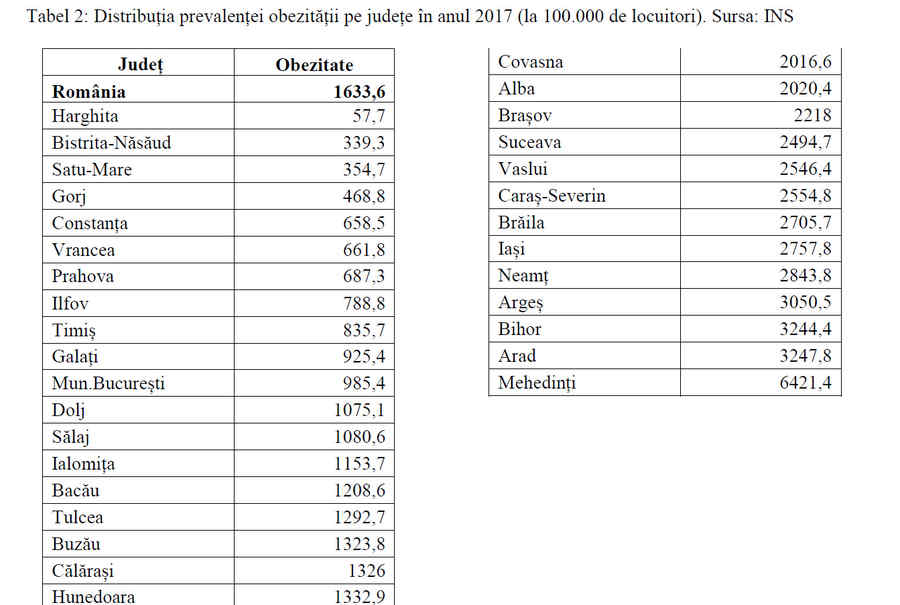
In Romania, the highest prevalence of obesity, in 2017, was in the counties of Mehedinți, Bihor, Arad, Argeș and Neamț, and the lowest in Harghita, Satu Mare, Bistrița-Năsăud and Gorj. Bucharest is somewhere in the middle of the ranking “, says the surgeon Mihai Ionescu.
Why obesity is on the rise
The number of overweight and obese people has increased in recent years and many people find it increasingly difficult to maintain a “normal” weight in today’s largely obese environment.
“The obese environment is stimulated by several factors: low breastfeeding rates, it is easier and cheaper to buy unhealthy foods than some with ingredients dedicated to a healthy diet, it is cooked less at home, there are more and more foods rich in energy on the shelves, we have a lifestyle and work schedule that prevents us from having regular and healthy meals or exercising.
According to the WHO, specific recommendations for a healthy diet include: eating more fruits, vegetables, nuts and grains, reducing salt, sugar and fat. Poor nutrition can lead to reduced immunity, increased susceptibility to disease, and poor physical and mental development.
Obese people more often develop high blood pressure, diabetes and atherosclerosis, which translates into increased risk of cardiovascular disease. The International Heart Federation showed in 2017 that 21% of ischemic heart disease can be attributed to excessive body weight.
Across the European Union, six of the seven most common risk factors for premature death are high blood pressure, hypercholesterolemia, high body weight, inadequate consumption of fruits and vegetables, lack of physical activity and alcohol abuse, “concludes surgeon Mihai Ionescu.
For most obese patients, the solution to get rid of extra pounds and major life-threatening risks is bariatric surgery.
Bypassul gastric
“Gastric bypass is a partial short circuit of the small intestine, through a laparoscopic approach, in order to treat obesity and its associated diseases.
Gastric bypass is designed for obese patients with a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher, or 35-40, accompanied by comorbidities such as sleep apnea, diabetes, osteoarthritis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, high blood pressure or metabolic syndrome.
The surgery is minimally invasive (laparoscopic), and the hospital stay is short (12 nights).
Recovery is rapid, the pain is less than in open surgical procedures, and the scars are barely visible.
Mihai Ionescu is a primary care physician in general surgery, with competence in obesity, oncological, laparoscopic surgery and pelvic floor surgery. He is a member of the Romanian College of Physicians, the Society of Surgery, the Romanian Association of Endoscopic Surgery (ARCE), the European Association of Endoscopic Surgery (EAES) and the General Medical Council (GMC-UK). He currently heads the general and metabolic surgery department of Medicover Hospital in Bucharest.
–


:quality(80)/cdn-kiosk-api.telegraaf.nl/62b0bce6-d8f1-11eb-98ef-0217670beecd.jpg)
