Dr. José Antonio Posada Torres
Oncologist Surgeon. Specialist in advanced laparoscopy and robotic surgery. Specialist in cancer of the ovary, endometrium, uterus – “Cancer in Women”. It is recognized as
one of the best specialist doctors in Oncological Surgery.
Hospital ABC Observatorio. Office 505 Torre Mackenzie
Office: 5572618980 or 5572619105
Instagram: @ surgeon.oncologist.cdmx
Twitter : @dr_posada
ON THE UTERUS
The uterus is part of the female reproductive system.
It is the organ where the fetus grows and develops.
It turns out that, during the menstrual cycle, if there is no pregnancy, hormonal changes cause the endometrium to detach and expel itself every month, that is, menstruation).
What parts make up the uterus?
It is shaped like an inverted pear and is in the pelvis between the rectum and the bladder. It is made up of two parts:
Cervix or cervix: the lowest area, which is inside the vagina
Body of the uterus: the widest part, which is above the neck. This part of the uterus has two layers. The innermost is called the endometrium. Outside is the muscular layer or myometrium, with the ability to contract during childbirth.
Sarcomas uterinos
They originate in the muscle layer (myometrium)
They represent only 10% of uterine cancers.
It is a rare tumor
Its benign counterpart is fibroids, which are present in up to 70% of women.
The most common is leiomyosarcoma, which is an aggressive tumor with a poor prognosis.
The average presentation age is 40 years.
Risk factors are not well identified. Some assumptions may be previous pelvic radiation, or some hereditary factors.
THE MIOMAS ARE NOT PRECURSORS. However, the size, growth and time of evolution force us to have the suspicion
Symptoms: bleeding, pelvic pain, palpable tumor.
Diagnosis: The studies are ultrasound and / or MRI
Treatment is surgical
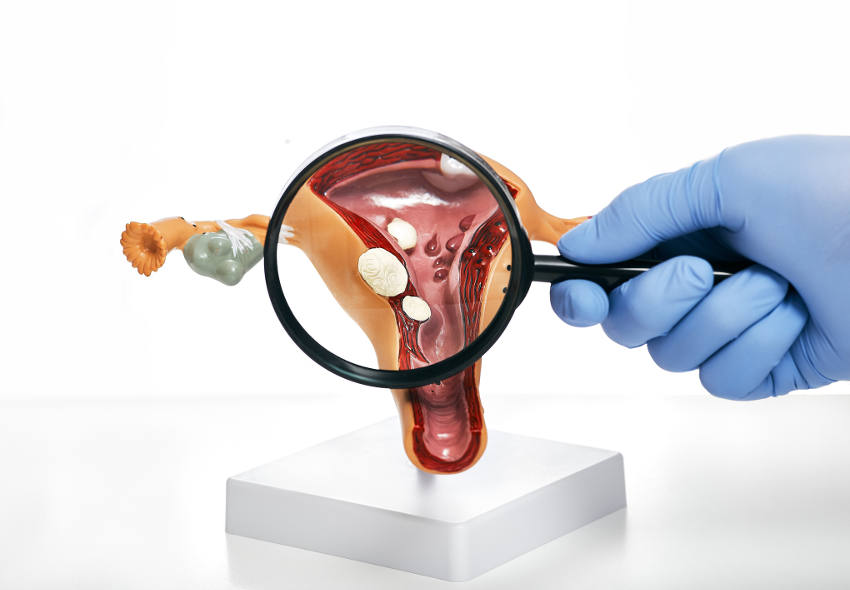
Fibroids
They are non-cancerous tumors.
They are not associated with an increased risk of uterine cancer and almost never turn into cancer.
They vary in size: from undetectable to the human eye to bulky masses that can distort and enlarge the uterus.
You can have just one or more.
Many women have fibroids at some point in their life. However, you may not know you have them because they usually don’t cause symptoms.
Some symptoms you may have:
Heavy menstrual bleeding
Menstrual periods that last longer than a week
Pelvic pressure or pain
Need to urinate often
Difficulty emptying your bladder
Constipation
Back or leg pain
Treatment
There is no single recommended approach to the treatment of fibroids, but there are many therapeutic options. It’s best to talk to your doctor about your options.
ABOUT ENDOMETRIUM
It is a mucous tissue made up of many blood vessels and glands that are destroyed and regenerated every 28 days.
Its function is to allow the implantation of the fertilized egg that will later become an embryo.
When this does not happen, it comes off and leads to menstruation.
Depends on estrogen stimulation
Normal size: from 0.6cm to 1 cm depending on the time of the cycle (day 19-21)
Endometrial cancer
It is the most frequent gynecological malignant tumor in first world countries and the second place in developing countries (1st place cervical cancer)
Endometrioid adenocarcinoma represents the most common type
It occurs mostly in post-menopausal women.
Symptoms: abnormal bleeding only 2-5% occurs in young women!
Risk factor’s:
obesity (excess endogenous and exogenous estrogens)
Metabolic diseases
chronic anovulation.
Diseases associated with genetic factors
Use of tamoxifen in patients with breast cancer
Hiperplasia endometrial
Diagnosis is made by ultrasound or pelvic tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. A hysterectomy (resection of the uterus completely) or a diagnostic curettage is done.
The most common tumors in the endometrium are divided into Type 1 and Type 2
Type1: 80% of cases, generally grade 1 or 2, generally have a better prognosis, depend on the stimulation of hormones and generally originate from a premalignant lesion such as hyperplasia
Tipo2: 10-20% of cases, grade 3, include tumors with a poor prognosis.
Treatment:
In early stages it is always surgical and the prognosis will depend on the extent of the disease.
There is a greater predisposition to present this disease in patients with a history of ovarian or colon cancer.
Lynch syndrome: autosomal dominant disease responsible for at least 20% of colon cancer cases and 3% of endometrial cancer.
Prevention: annual visit with transvaginal ultrasound (in case of having started sexual life) and knowing risk factors
–