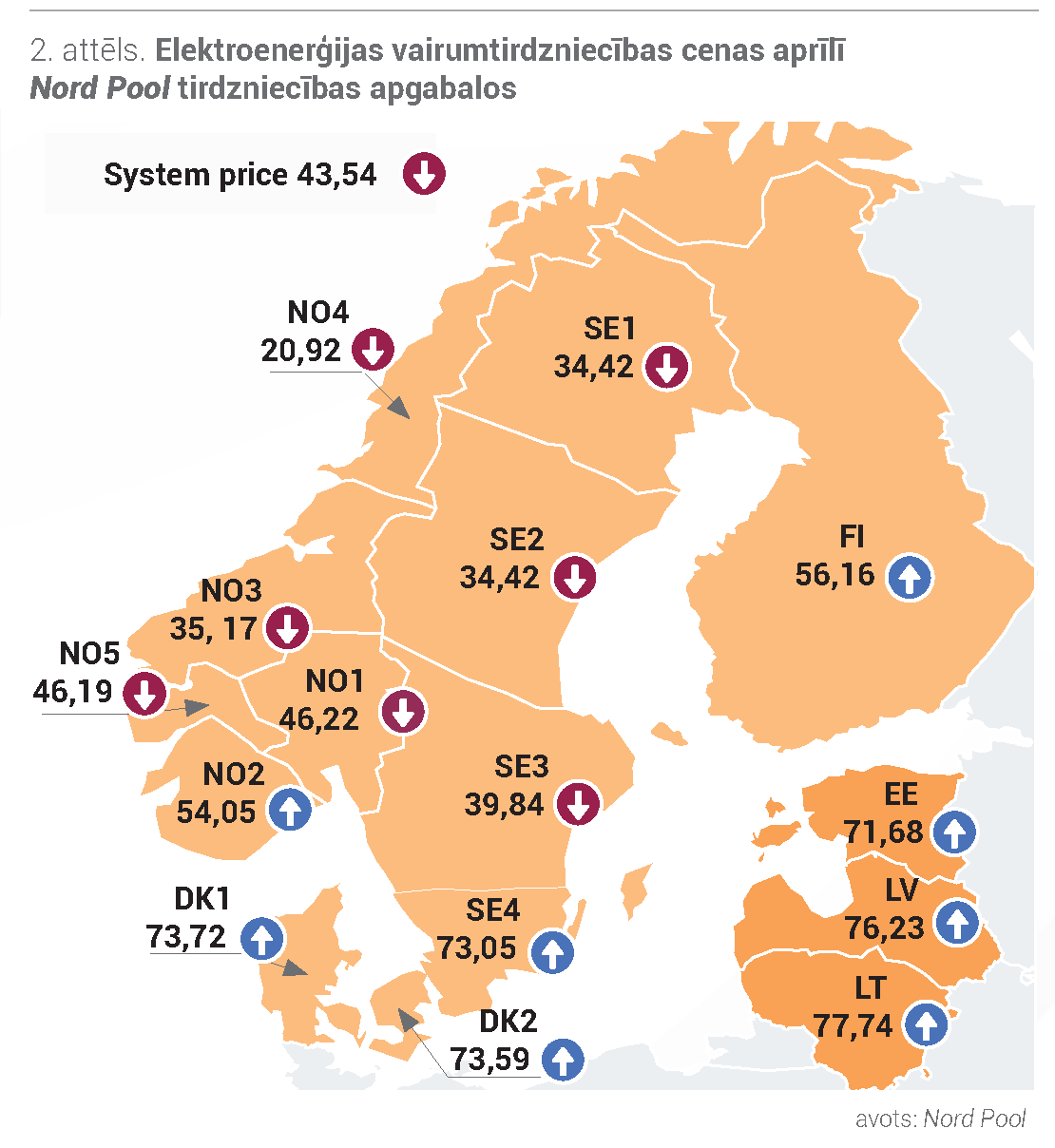
In June, Nord Pool had different trends in average monthly electricity prices in different trading areas, resulting in a 2% decrease in the average system price to EUR 43.54 / MW. The highest electricity price among the Baltic States was in Lithuania – 77.74 EUR / MWh, which increased by 54% compared to May. In Latvia, the average monthly electricity price was 76.23 EUR / MWh, which increased by 57% compared to May. The price of Estonian electricity increased by 48% and was 71.68 EUR / MWh. In the Baltics, the hourly price range ranged from 1.00 EUR / MWh to 255.00 EUR / MW.
–
–
Content will continue after the ad
Advertising
–
In June, warm weather was observed not only in the Baltics, but also elsewhere in Europe. This contributed to a 4% increase in demand in the Nord Pool region as a whole compared to June last year. Drier weather conditions were observed last month. This had an impact on total electricity generation in the region, which decreased by 11% compared to May. The price of electricity in June was also affected by the lower development of wind farms, which decreased by 13% in the Nord Pool region and by 55% in the Baltics compared to the previous month. Due to low wind power plant development and low rainfall, the snowmelt season in Scandinavia has not affected electricity prices this year. Also in June, the annual maintenance of nuclear power plants in the Nordic countries continues, which reduced the volume of nuclear power plant development.
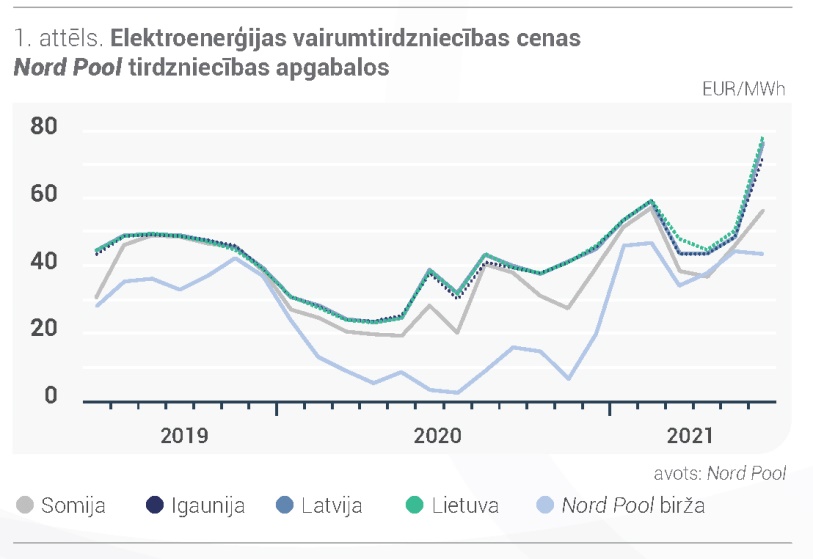
The price level in the neighboring countries also had an impact on the Baltic electricity prices. In June, energy flows from Finland increased by 22%, thus contributing to the lowest electricity price in the Baltics in the Estonian trading area. At the same time, flows from Sweden’s SE4 area were only 4% lower than a month earlier, which contributed to the highest price in the Baltic trade area in the Baltics. In addition, the rise in Baltic prices was also influenced by energy flows from Russia, which fell by 41% last month.
Electricity futures prices are affected by hydro balances and raw material markets
In June, future contract price movements were affected by both the rising price trend in the commodity and allowance markets and the state of the Nordic hydropower balance. In the first half of June, the hydro balance was on a downward trend, falling to -3.6 TWh. In the middle of the month, the situation improved due to higher precipitation, and this was reflected in the increase of the hydro balance to 0.9 TWh. However, with the resumption of hot and dry weather, the hydro balance dropped below normal at the end of the month and was -5.8 TWh. Last month, the Nordic snow stocks were below normal and decreased by 67% compared to May.
July futures contract for the electricity system (Nordic Futures), the average price increased by 17% to 39,63 EUR / MWh in June. The average price of the system’s contract for the 3rd quarter of 2021 increased by 11% to 39.19 EUR / MWh, the closing price of the contract at the end of the month was 42.40 EUR / MWh. In June 2022, the average price of the futures system decreased by 3% and was 31.18 EUR / MWh, at the end of the month the contract price was 30.55 EUR / MWh. Last month, the average price of Latvian electricity futures for the July futures contract increased by 11% and was 65.73 EUR / MWh, the closing price of the contract was 76.75 EUR / MWh. In June, the price of Latvia’s “futures” in 2022 increased by 2% to 55.15 EUR / MWh, at the end of the month the contract ended with a price of 56.80 EUR / MWh.
In the Baltics, demand increased and development volumes decreased
Last month, electricity consumption in the Baltics increased by 2% compared to June a year earlier, and a total of 2018 GWh of electricity was consumed. In Latvia, consumption increased by 3% to 546 GWh compared to June 2020. According to the Latvian Center for Environment, Geology and Meteorology, the average air temperature in Latvia in June was + 18.9 ° C, which is 4.1 ° C above the monthly norm, thus last June was the warmest in the history of observations (since 1924). In terms of air temperature, several records were exceeded in Latvia last month, which undoubtedly led to more active use of air conditioning equipment, and this also had an impact on electricity consumption. Lithuania also saw an increase in electricity consumption of 4% in June, with 942 GWh of electricity consumed. In turn, the amount of electricity consumed in Estonia was 530 GWh, which is a decrease of 4% compared to June last year.
Electricity production in the Baltics decreased by 9% in June compared to May and by 13% compared to June 2020. A total of 1,077 GWh of electricity was generated in the Baltics last month. In Latvia, production volumes decreased by 34% to 347 GWh compared to the previous month. Lithuania, on the other hand, generated 346 GWh of electricity in June, which was 2% more than in May. In Estonia, electricity generation increased by 21% to 384 GWh.
In June, the ratio of total production to total electricity consumption in the Baltics was 2% lower than in the previous month – 53%. In Latvia, the ratio of total generation to monthly consumption decreased and amounted to 64%. In Lithuania, in June, this indicator remained at the level of the previous month and was 37%. In Estonia, on the other hand, it increased and was 72%.
The development of the Daugava HPP has decreased
In June, due to hot and dry weather, the average inflow into the Daugava decreased by 56% to 411 m3 / s compared to May. However, it remained at the level of June of the previous year and was 18% higher than the multi-annual average inflow level. The deterioration of the hydrological situation was influenced by the decrease in the total amount of precipitation in Latvia, which was 44% below the monthly norm in June. The above data were also reflected in the volume of electricity generation at Daugava hydropower plants, where 181 GWh was produced in June or by 57% less than in May. At the same time Latvenergo The development of thermal power plants increased and 92 GWh of electricity was generated. TEC The increase in development was determined not only by the decrease in HPP development, but also by higher market demand.
Several price records have been set in the energy product markets
In June, the price of Brent Crude Futures’ crude oil futures contract generally showed an upward trend. On average, it increased by 8% to 73.23 USD / bbl and ended at 75.13 USD / bbl at the end of the month.
Oil prices Growth last month was driven by strong economic growth and, consequently, oil demand. Oil production by OPEC + member states will continue to grow in June, but at the same time oil supply from China and the United States will decrease. Therefore, at the end of the month, the oil market focused on the meeting of OPEC + member states and the expected decision to increase oil production in August.
Coal futures contract (API2 Coal Futures Front month), the average price increased by 24% to USD 106.47 / t in June, and the contract closed at USD 120.75 / t, the highest price in 10 years.
Such growth in the European coal market at the beginning of the month was driven by strong protracted demand in Asia, as well as supply disruptions from Colombia and Russia. The dry and cold winter also had a negative impact on China’s hydropower production, which fell by 10% in the first 4 months of this year. As a result, there is now a shortage of energy in China, which is driving up demand for coal and thus leading to a sharp rise in the price of coal. The price of coal in June was also affected by the low development of renewable energy resources, as well as the market trends of related energy products.
Last month (Dutch TTF), the average price of a natural gas futures contract in July increased by 14% to EUR 28.35 / MWh. The contract price continued its upward trend, closing the month with a price level of 32.29 EUR / MWh, which had not been exceeded since 2008.
An important factor influencing the price of natural gas last month was the weather, which ensured the development of lower wind power plants. The planned annual maintenance works in Norway will continue in June, which reduced Norway’s natural gas production and exports in the first half of the month. In addition, low supplies of liquefied natural gas (LNG) to Europe have been observed. “Nord Stream“The annual maintenance of the gas pipeline is planned for July, although its impact on the price of gas is already visible at the end of June. For the Russian energy company”Gazprom“Failed to reserve capacity for gas transit through Ukraine to Europe during repairs to the Nord Stream pipeline. Last year, Gazprom used gas from the storage to cover customer nominations, but this year it could be difficult to implement as the company’s storage in Europe is almost empty. Overall, the filling of European natural gas storage facilities remains low, at the end of the month it was only 47.5%, compared to 80.4% compared to June of the previous year.
In the first half of June, European emission allowances (USA Futures) was volatile, but showed a slightly upward trend in the second half of the month. On average, the EUA Dec. 21 contract price increased by 1% to 52.92 EUR / t.
The increase in the price of emission allowances was slowed down by the preliminary list of installations published by Germany, which will receive 129 million free allowances between 2021 and 2025. However, a small increase in the price of allowances on a monthly basis was driven by low development of renewable energy resources, higher demand for energy resources, and, as a result, higher demand in the allowance market. These factors were supplemented European Commission plans to set stricter requirements for reducing carbon emissions and meeting climate targets.
–


