the doctor did the operation. A biopsy was taken from the left lung. send for pathological examination Necrotizing granulomatous inflammation, tuberculosis not detected, stained yeast-like fungi was observed. Histoplasma capsulatum was cultured and the patient probably had histoplasmosis. By inhaling the spores of Histoplasma capsulatum after entering a tree cavity. causing the pneumonia to spread to the adrenal glands and spleen
Doctor Manoon It provides details of Histoplasmosis (Histoplasmosis) which is a disease caused by inhaling spores of the fungus Histoplasmacapsulatum, which is derived from bat or bird droppings into the lungs. And some people can spread to various organs like liver, spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow, adrenal glands, brain is a disease which is not common.
for mushrooms Histoplasma capsulatum It is commonly found in the environment, especially on soils contaminated with bird droppings and bats in tree holes. under a big tree or in a cave This type of pathogenic fungi are dimorphic fungi, in nature they live as fungi that can produce spores and when we inhale the spores into the lungs or infect the body. The infection looks like yeast.
This disease can be found in both normal and immunocompromised people. Especially those who have a history of hiking or visiting caves with large amounts of bird droppings or bat droppings without wearing protective equipment such as a face mask. The endemic areas of this disease are in the Americas, Africa and parts of Asia. While in Thailand, the prevalence has been found at 0.3-1%, with irregular outbreaks often seen in some areas in the western and southern regions of the country. immunocompromised people Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infected patients, AIDS patients, patients receiving immunosuppressant drugs, infants and the elderly.
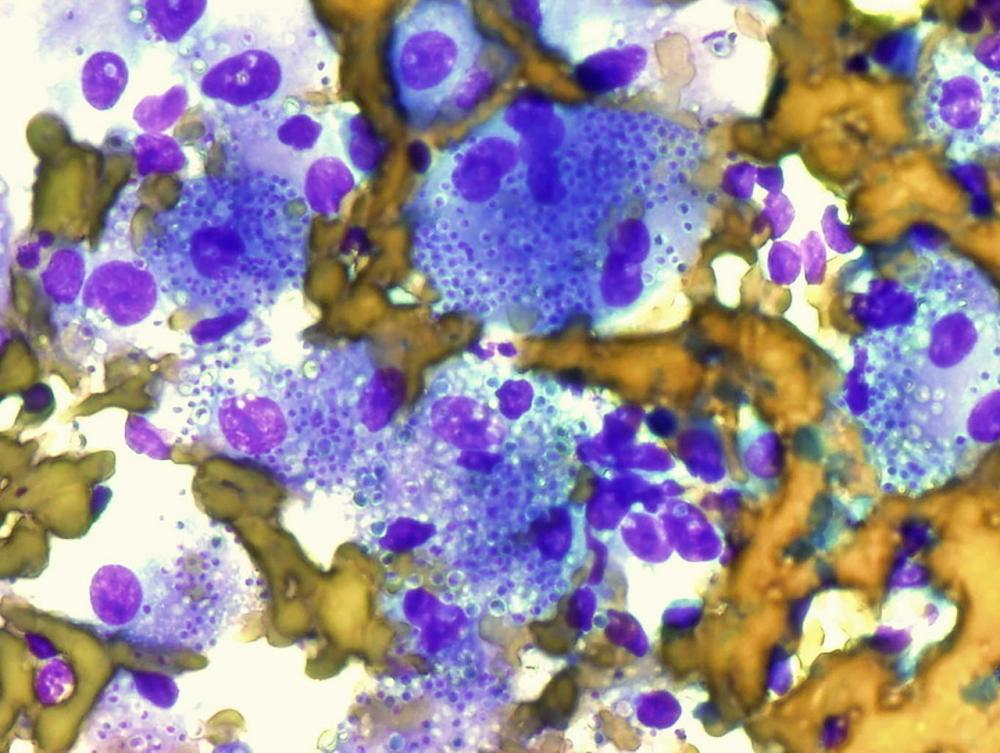
After inhalation of the spores The virus has an incubation period of 3-17 days. Most infected people usually show no symptoms, but in some cases only about 1% often show symptoms and symptoms. Usually this disease can disappear by itself within 2-3 weeks to 1 month. Patients may have lung infections, skin infections. or disseminated infection (disseminated histoplasmosis). The severity of the disease depends on the amount of infection received and the patient’s level of immunity. The most common symptoms include fever, headache, dry cough, fatigue, chills, chest pain and body aches. In some patients, skin rashes or joint pain may occur. Also, in those who already have lung disease, such as emphysema. it can be risky to chronic infections, including severe symptoms
There is currently no vaccine against the disease. In immunocompromised patients, acute pulmonary infections resolve spontaneously without medication. The main antifungal drugs in the treatment group are amphotericin B and itraconazole. The dosage and duration of administration depend on the severity and clinical characteristics of the disease. Also, some patients may need surgery if nearby organs are obstructed or compressed.
The best prevention is to avoid traveling to areas where there is a risk of infection or a high prevalence of the disease. If you have to travel, you should wear a hygienic mask. Wear gloves or protective clothing and wash your hands regularly.
When working in areas with a lot of bird or bat droppings The area should be well watered to reduce the spread of droplets, manure or soil which may be contaminated with spores. Protective equipment such as masks and gloves must be worn. Before any work, symptoms or abnormalities should be observed. After visiting forests or caves and in areas with high levels of bird or bat droppings If you experience any unusual symptoms or discomfort, you should seek immediate medical attention.


.jpg)