Key Highlights
- Exports in Jan. negative 4.5%YoY continued to decline for months. 4 This is more than the market’s expectation of -1.0% due to the impact of the global economic slowdown. The purchasing power of consumers in trading partner countries remains weak. The contraction was in the same direction as other countries in the region. As a result, the export of agricultural products agro-industrial products and industrial goods contracted
- Krungthai COMPASS It is estimated that exports will continue to shrink for a while. This is because many of the main export products will still be affected by the weak global economy. Including rebalancing inventory levels after demand for products that were previously affected by COVID-19. exports in the future Therefore, it is still facing pressure and there is a chance that the value of exports in 2023 may be lower than the previous estimate. and has a chance to expand at a negative rate

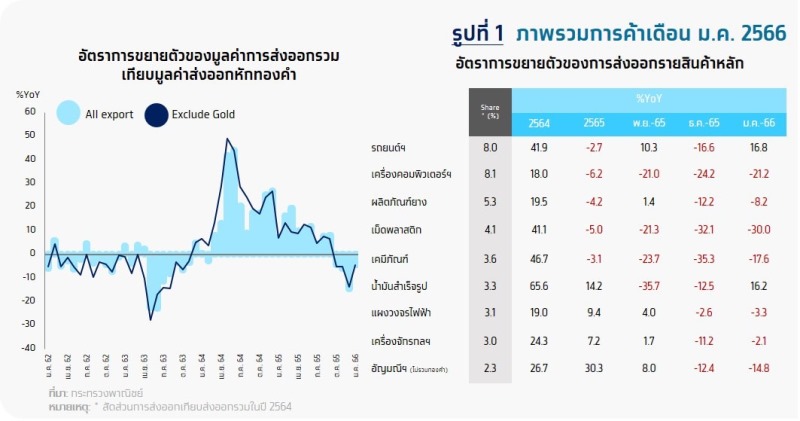
Export Value January 20136 Shrinkage 4.5%
The value of exports in January is 20,249.5 million dollars, contracting 4.5%YoY, continuing to decline year-on-year for the fourth month. However, the export of both agricultural products. agriculture industry and industries are shrinking Due to the impact of the global economic slowdown and the purchasing power of consumers in trading partner countries remains weak amid high inflationary pressures. The contraction was in the same direction as other countries in the region. As for gold exports, this month continued to contract by -14.8%. This month’s export value contracted 4.4%YoY.
Exportlist of productsMost of them continued to decline.
- exports of industrial goods contracted 4 months in a row at -21.7%YoY, contracting more from the previous month, which contracted 7%YoY. from exports of plastic resin (-30.0%), chemicals (-17.6), computers and parts (-21.2%), rubber products (-8.2%), and gems and jewelry (-3.8%). However, some products could expand. Especially cars, equipment and components. which returned to growth again (+9.2%), while some key exports continued to expand, such as semiconductors, transistors and diodes (+73.3%), motorcycles and components (+16.4%), and transformers and components. (+44.9%) etc.
- Exports of agricultural products and agro-industry continued to contract for a month. 4 at -7%YoY, but down from the previous month’s contraction of -11.2%. Many major products continued to contract, such as sugar (-45.4%), rubber (-37.6%), cassava products (-7.6%), canned and processed seafood (-4.8%) and processed chicken (-2.2%). Some products continued to expand well, including rice (+72.3%), fresh/chilled/frozen chicken (+50.0%) and fresh fruits (+2.5%).
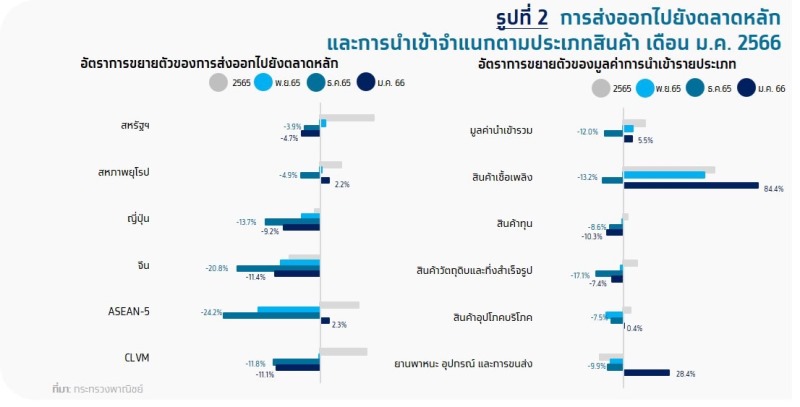
Exportby marketmostly shrink
- United States : contracted for the second consecutive month at -4.7%YoY, with significant contraction in computers equipment and components, rubber products and clothing, etc., while products that expand include semiconductors, transistors and diodes, transformers and components. and fax machines, telephones and components, etc.
- China : contracted for the 8th consecutive month at -11.4%YoY, with significant contraction in computers equipment and components, plastic pellets and automobiles, equipment and components, etc. Products that expanded were rubber products, chilled and frozen chicken. and refined oil, etc.
- Japan : It contracted for the fifth consecutive month at -9.2%YoY, with the major contractors being chemicals, processed chicken, and copper, etc. The expansion of products included electronic circuit boards, motorcycles and parts, and cars, equipment and parts, etc.
- EU27: Returned to grow at +2.2%YoY, with the key products expanding, including gems and jewelry. Air conditioners and components and electric transformers, etc. The products that contracted were rubber, rubber products, automobiles, equipment and parts, etc.
ASEAN5 : Recovered to grow at +2.3%YoY, mainly driven by automobiles, equipment and parts. gems and jewelry, and rice, etc. The products that contracted were plastic beads, rubber, and electronic circuit boards, etc.
The value of imports in January was 24,899.1 million dollars, returned to grow 5.5%YoY from the previous month’s contraction of 11.9%YoY. This was driven by growth in imports of fuel products (+84.4%YoY), vehicles and transportation equipment (+28.4%YoY), and consumer goods (+0.4%YoY), driven by a gradual normalization. increase in domestic economic activities in line with the continued recovery of the tourism sector Meanwhile, imports of capital goods (-10.3%YoY) and raw and semi-finished goods (-7.4%YoY) contracted in line with the contraction in production for export. The December trade balance posted a 10th straight month deficit at -$4,649 million.
 Implication:
Implication:
- Consecutive contraction in the value of Thai exports in the past This was mainly due to the industrial sector that faced pressure from the global economic slowdown. This was partly due to weak purchasing power in trading partner countries. Including concerns about the global economic recession that affects demand for many major industrial products such as electrical appliances. construction materials and jewelry, together with the consequences of the problems of the Chinese economy that has not fully recovered. Pressure on exports in the plastics and chemicals group that rely on the Chinese supply chain. At the same time, computer exports are still facing the down cycle of electronics products. These factors resulted in a 8%QoQ contraction in Thai exports in the fourth quarter of 2022, with the above-mentioned industrial products accounting for 9% of the total and a combined 5.2% contraction.
- Krungthai COMPASS estimates that exports are likely to contract for a while. This is because many major export products will still be affected by the global economic slowdown. Including rebalancing inventory levels after demand for products that were previously affected by COVID-19. In particular, work-from-home-related products declined, which resulted in some products tending to be in a downward cycle, such as computers and electronic devices. While the Chinese economy has not fully recovered and may have to wait for a clear improvement in the second quarter of 2023. in the future Exports are therefore still facing pressure and there is a possibility that the value of exports may expand at a negative rate. Thai export figures in 2023 may therefore be lower than the previous estimate.


