KOMPAS.com – The body of a living being consists of various kinds of cells and organelles, one of which is the cell cytoskeleton or so-called cell skeleton.
The cell cytoskeleton or cell skeleton is a structural cell that fills the cytoplasm and plays a role in cell movement (motility) and cell stability.
The cytoskeleton itself is further divided into three main fibers, viz microfilament, microtubules, and filamentous intermediates.
3 types of cytoskeletal cells
Microfilaments are the smallest cytoskeleton protein fibers that function as a pathway for the movement of motor proteins called myosins (which form filaments).
The type of protein that makes up the microfilament cell skeleton is actin.
Also read: Role of Soil Microorganisms
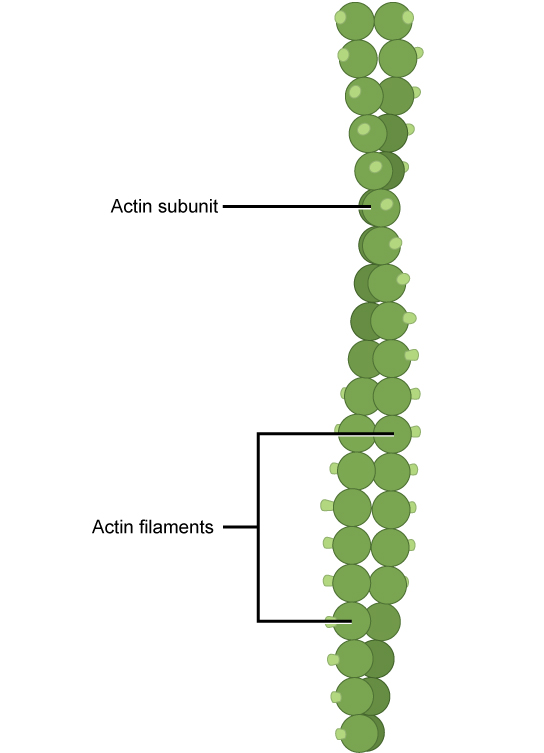
Structure microfilaments
–
Report from Dictionary of Biology, the microfilament structure consists of two subunits of the actin protein chain (globular) and has polarity at the ends.
The two actin strands are wound with each other to form a spiral microfilament.
Microfilaments are fine, thin, long fibers with a diameter of only about 3 to 7 nanometers, so they are called the smallest cytoskeleton protein fibers.
Microfilament function
Some of the functions of microfilaments are as follows:
Report from University of Arizona Biology ProjectThe microfilaments and myosin proteins are responsible for muscle contraction.
Also read: Groundwater in the Hydrological Cycle
The collaboration between microfilament actin and myosin is called actomyosin which allows muscles to contract and relax and allows cell movement.
This actomyosin allows single-celled animals such as amoebae to move around.
Microfilaments function in cell stability as structures that maintain and preserve cell shape.
Its ability to build muscle contraction makes microfilaments play an important role in cytoplasmic flow.
Microfilaments contract to flow the cytoplasm in the form of nutrients, waste, and other materials to areas of the cell where these materials are needed.
From the image of the cytoskeleton cells, it can be seen that the microfilaments are on the outside that surrounds the cell.
This causes contraction of the microfilament splitting the cell in half.
When DNA replication is complete, the microfilament will narrow in the middle, break up, and slowly form two distinct cells.
Also read: Soil Degradation: Definition and Classification
Microfilament Characteristics
The characteristics of microfilaments are:
- The fibers are 3-7 nanometers in diameter
- Consists of two strands of actin protein
- Long spiral shaped
- Around the edge of the cell
- It consists of thin filaments and thick filaments that weave salts on
- There are thicker filaments along the muscle cells
–

:quality(80)/cdn-kiosk-api.telegraaf.nl/ce71b38c-9b74-11eb-b431-0255c322e81b.jpg)