KOMPAS.com – In studying pressure, there is what is known as partial pressure. The pressure exerted by a given gas in a mixture of gases is called the partial pressure.
However, what exactly is partial pressure and how do you determine partial pressure? Here is the explanation!
Definition of partial pressure
The gas can be present in its pure form or in a mixed form along with other gs. Reported from Thought Coeach gas in the mixture contributes to the total pressure of the mixture.
Each gas in the mixture exerts an individual pressure which is known as partial pressure. The concept of partial pressure was first proposed by a British meteorologist and chemist named John Dalton.
Also read: Contents of Dalton’s Atomic Theory
Dalton’s idea stems from the high density and compressibility of gases because gases consist mostly of empty space.
Reported from Lumen LearningDalton concluded that when two or more different gases occupy the same volume, then they will behave completely independently of each other.
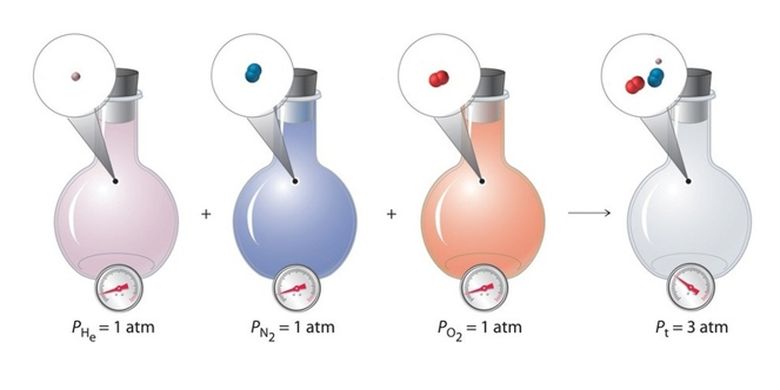
That is, a mixture of unreactive gases is not affected by the forces of attraction or repulsion between the constituent gases. At the same temperature and volume, the partial pressures of each constituent gas form the total pressure of the gas mixture.
Dalton’s law of partial pressure says
This concept is known as Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressure. Reported from Chemistry LibreTextsDalton’s law of partial pressure reads:
“The total pressure exerted by the gas mixture is the sum of gas partial pressure component”.
Also read: Factors Affecting Gas Pressure
For example, Earth’s atmosphere is a mixture of gases consisting of nitrogen, oxygen, argon, carbon dioxide, and other gases. The total pressure of Earth’s atmosphere is the sum of the partial pressures of nitrogen, argon, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and all the other gases that make up the atmosphere.
The formula for the total pressure of the gas mixture
Dalton’s law of partial pressure can be formulated into a mathematical equation:
With,
Ptot: total pressure of gas mixture
P1: partial pressure of the first gas
P2: the partial pressure of the second gas
P3: Gas pressure third
Also read: Molecular Mass and Ideal Gas
The formula for total pressure two ideal gas
Dalton’s law of partial pressure can also be applied to a gas mixture consisting of two ideal gases. Following the formula gas pressure ideally, the Dalton equation can be written as:
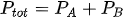
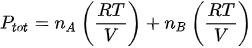
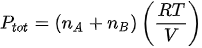
With,
Ptot: total pressure of gas mixture
nA: number of moles of gas A
nB: jumlah mol gas B
R: constant gas ideal (8,134 J / molK)
V: volume campuran gas
Also read: Mol Concepts and Avogadro Settings
The amount of a gas in a mixture can be expressed in terms of mole fraction. The mole fraction is the ratio of the number of moles of a gas to the number of moles of the gas mixture. Thus, the partial pressure can also be calculated as follows:
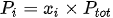
With,
Pi: gas partial pressure
xi: mole fraction of gas
Ptot: total pressure of gas mixture
Get updates news of choice and breaking news every day from Kompas.com. Let’s join the Telegram group “Kompas.com News Update”, how to click the link https://t.me/kompascomupdate, then join. You must first install the Telegram application on your cellphone.–