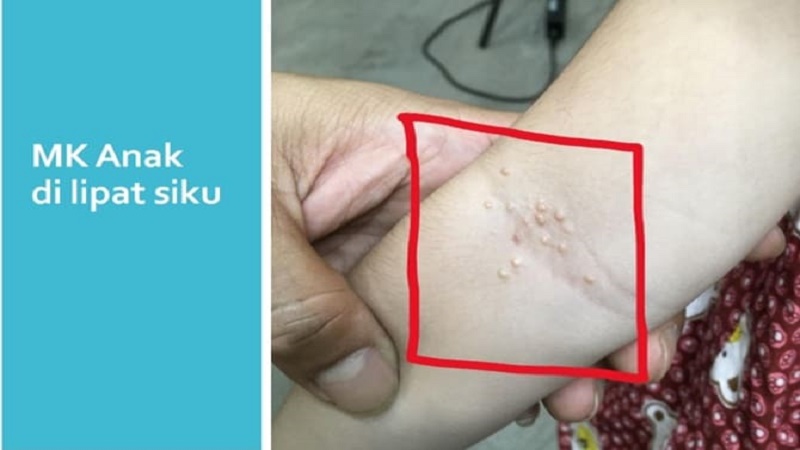
Skin disease of rashes similar to pimples and spreads on the body, don’t underestimate it. It could be that it is a type of molluscum contagiosum skin disease. The disease is a skin infection caused by the pox virus.
The virus can survive on surfaces that have been touched by an infected person’s skin. Thus, transmission can also occur in contaminated goods.
“Molluscum Kontagiosum is a highly contagious viral infection and can be transmitted from person to person through skin-to-skin contact, sharing of clothing, or simply by touching objects that are touched by an infected patient,” said Dermatologist and Venereal Specialist dr. Anthony Handoko, SpKK, FINSDV from the CEO of Pramudia Clinic in Virtual Media Briefing, Wednesday (4/11).
Molluscum Kontagiosumi causes small bumps on the skin that are usually painless but can cause itching. Usually it can disappear on its own and does not leave a scar, even if it is not treated.
“Usually children get infected when they play with their friends. In adulthood, it is usually transmitted through sexual contact or contact while exercising, ”he added.
He continued the MK incubation period between 2-6 months. However, MK early detection is not easy. Apart from rarely itching, in general MK does not have pain. The clinical form of MK symptoms on the skin almost resembles acne and is rapidly becoming numerous.
“In children, MK is often found on the chest, back, legs, hands, folds and face. Meanwhile, adults are found in the genitals and the surrounding area, ”he said.
To prevent infection from the MK virus, apart from avoiding physical contact with sufferers, people need to always maintain health and immunity, and always maintain cleanliness.
Avoid contact with sufferers. Wash your hands with warm water and soap. Teach children to wash their hands properly, especially after playing and interacting with other people. Avoid sharing personal items, such as towels, clothes, combs, and bar soap. Avoid sharing sports equipment that comes into contact with others, such as gloves and helmets. Avoid touching the bumps.
–
Treatment
If treated properly and there is no re-contact with the source of infection, recurrences are rare in MK. There are several treatment modalities for MK. It’s just that in practice, treatment in children is much more difficult than in adults.
Here are some MK treatments:
Cryotherapy, which uses liquid nitrogen to freeze each lump.
Curette, which is using a tool to penetrate the bump and scrape it.
Laser therapy, to destroy each lump.
Topical therapy, using creams containing acids or chemicals in order to exfoliate the top layer of the skin. This therapy can cause pain and therefore requires anesthesia. Therapy for patients with low immunity will be longer and more difficult.
Apart from therapy, doctors also usually suggest other treatment methods for molluscum contagiosum,
–
namely smearing the nodule with trichloroacetic acid, salicylic acid, or tretinoin, either in cream form
or ointment.
Curette or scraping, namely by scraping the nodules using a special medical instrument. Diathermy, which is to destroy the nodule using heat energy, by first being given a local anesthetic.
In people with molluscum contagiosum who have large or quite a lot of nodules, the doctor will usually repeat the procedure every 3 or 6 weeks until the nodules disappear. During treatment, new nodules can still appear, but usually will completely disappear within 2-4 months after treatment.
– .