Input 2021.02.16 06:00
It seems to be mass-produced in the 4nm process operating in the second half of the year
Superiority in microprocessing competition with TSMC–
–
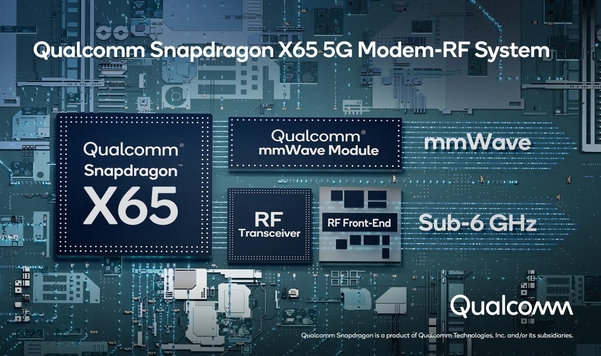
According to the semiconductor industry on the 16th, Qualcomm’s latest 5G modem chip, the Snapdragon X65, is produced in a 4 nanometer (nm·1 nanometer is 1 billionth of a meter) process and will be installed in smartphones scheduled to be released in the second half of this year. The modem chip is a semiconductor used to send and receive data in a smartphone. In the case of the X65, it is the first 5G chip to achieve a data transmission rate of 10 Gbps (10 gigabits per second). This is 100 times faster than the 4th generation mobile communication, Long Term Evolution (LTE).
Qualcomm is already producing the Snapdragon 888, a mobile application, solely by the Samsung Electronics foundry. The Snapdragon 865, the previous-generation premium mobile AP, was made with TSMC’s 7-nano process, but from the next generation, only Samsung Electronics foundry is being used. It was analyzed that Qualcomm recognized Samsung Electronics’ competitiveness in microprocessing.
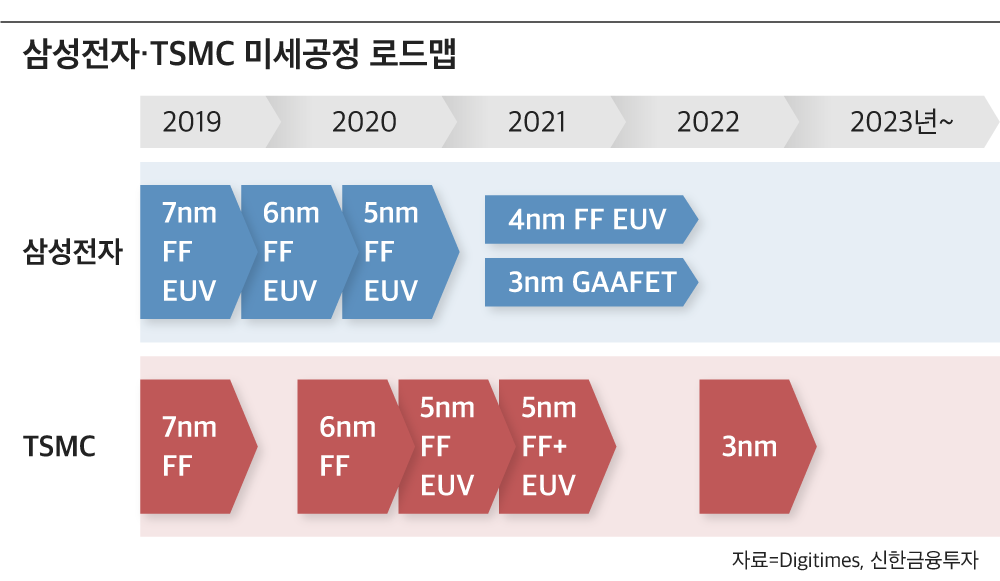
In the case of 5G modem chips, Taiwanese TSMC and Samsung Electronics have been separately producing 5 nano processes. However, from the X65, which is applied with 4nm, Samsung Electronics is expected to receive exclusive orders as well as mobile APs. Looking at the current process introduction roadmap, TSMC may find it difficult to produce 4nm process modem chips in the second half of this year.
–

–
Samsung Electronics has completed the development of the first-generation 4-nano process (LPE, Low Power Early) and is expected to begin mass production in the second half of this year. In addition, the development of the second-generation 4-nano LPP (Low Power Plus) process has also begun. TSMC is also developing a 4-nano process, but the industry predicts that mass production will be a little later than Samsung Electronics.
Samsung Electronics and Qualcomm were in an uncomfortable relationship just three years ago. In 2016, the Fair Trade Commission conducted an investigation saying that Qualcomm abused the’mobile communication standard essential patent’, and Samsung Electronics took the part of the Fair Trade Commission. As such, Samsung Electronics has been hostile to Qualcomm regarding patents. In addition, in a patent abuse lawsuit in the United States, Samsung Electronics criticized Qualcomm through a written opinion.
Then, in January 2018, the two companies agreed to expand the’global patent cross-licensing agreement’ and closed the conflict. After that, Qualcomm, which does not have a semiconductor factory (fab), started entrusting semiconductor production to the Samsung Electronics foundry. A representative example is the Snapdragon 765, which was produced by Samsung Electronics’ foundry in 2019 through a 7-nano process.
Samsung Electronics installed the Snapdragon 865 on its flagship smartphone Galaxy S20. The Snapdragon 865 is a mobile AP made with TSMC’s 7-nano process, and it was evaluated that it was unusual for Samsung Electronics to incorporate Snapdragon to the Galaxy sold in Korea. This is because Samsung Electronics used Exynos as much as the Korean Galaxy. An industry insider said, “The installation of the Snapdragon on the Galaxy for sale in Korea surprised the employees of Qualcomm’s headquarters.”
–
–
However, even with the introduction of the 4-nano process, securing the yield (the ratio of good products to all products) is the key. The industry points out that if the yield of the 4-nano process is not sufficiently secured, winning a contract of several trillion won may not make any profit. An industry insider said, “Some pointed out that the yield of Samsung Electronics’ foundry’s 5-nano process is lower than that of its rival TSMC,” and said, “It can be said that securing the yield of not only 5 nanometers but also 4 nanometers is key.”
–
– .