Healthcare providers and persons who had unprotected high-risk contact with a person infected with monkeypox can be vaccinated against monkeypox, preferably within four days of the contact.
Belgium already had 200 doses of Imvanex from the Danish company Bavarias Nordic. This vaccine is licensed in the European Union against classical smallpox, but can also be used against monkeypox. Our country has also received 3,040 doses of the Jynneos vaccine. That is the American version of the Imvanex vaccine.
For whom?
“Due to the limited number of vaccines and the current uncertainty about extra deliveries, this vaccination is done under strict conditions,” emphasizes Health Minister Frank Vandenbroucke. This concerns healthcare personnel after a high-risk contact without protection, immunocompromised after a high-risk contact (such as an infected family member or sharing clothing with a patient with a rash), and persons after a very high-risk contact (such as sexual contact or prolonged skin-to-skin contact with a person with a skin rash or wound).
The vaccine should preferably be administered in the upper arm within 4 days of exposure. People who have been vaccinated against classical smallpox are in principle not re-vaccinated, unless they have an immune disorder. Those who have not been vaccinated against classical smallpox should receive a second dose at least 28 days apart. The vaccines are administered in nine reference centers in our country.
Anyone who thinks they have had high-risk contact should contact their general practitioner or attending physician, who can then consult with the reference center on whether vaccination is useful.
Men
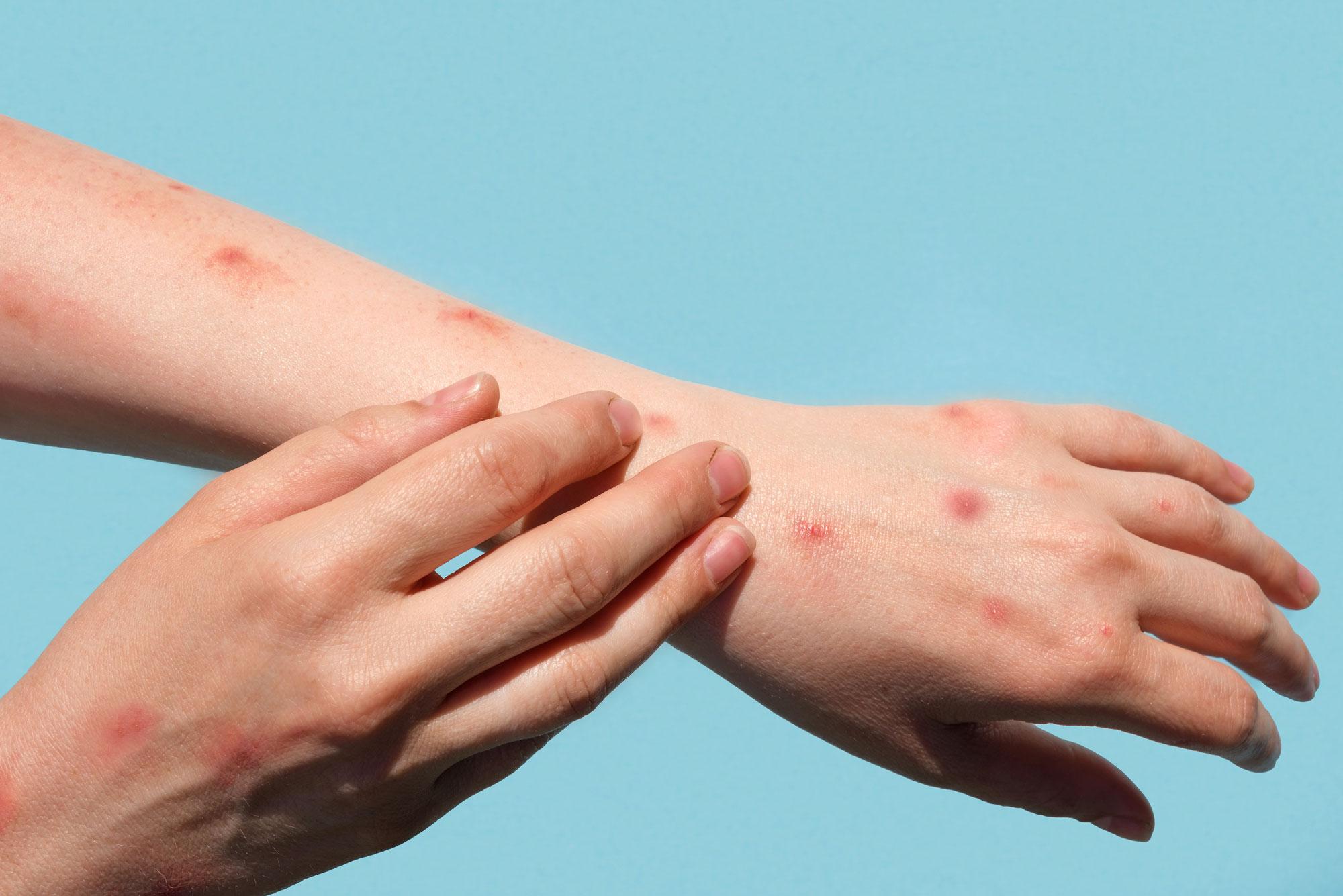
Since the beginning of May 2022, cases of monkey pox have been reported in Belgium, as abroad, that have no link with a trip to West or Central Africa, where the virus circulates more often. On 5 July, Sciensano had 168 confirmed cases in Belgium: 92 in Flanders, 64 in Brussels and 13 in Wallonia. It’s all about men from 20 to 62 years old. The virus usually causes fever and typical skin lesions, similar to chickenpox. The lesions can appear anywhere on the body, including the face and palms. Most cases are mild and do not cause serious illness in healthy adults. Symptoms usually resolve spontaneously within two to four weeks.
–