The plan to produce reference designs (only) by early 2021 was confirmed on Twitter by Scott Herkelman, the company’s vice president of Radeon. If AMD does not plan to stockpile the cards in larger quantities at the beginning of the year, which will last for some time, then this is the first time in a very long number of years that the cessation of production of reference models can be regretted.
Throughout the history of the Radeons, there have been several periods when reference cards were required, in some cases valued more than non-reference. But the reasons used to be different. Even before the Radeon brand, with Rage cards in the second half of the 1990s, the main reason was the quality of the analog output. This was held by Matrox (the cards were produced almost exclusively by itself), 3Dfx on the Voodoo 3 series (the previous company did not produce by its own means) and ATi. Products made by partner companies – often with big name brands today – were often worthless, and if the user looked at something more than a 14 ″ screen in 640 × 480, even plain text looked like a daub, sometimes with colors or ghosts.
With Radeons (ie since 2000), the reason for the demand for reference cards has changed. The quality of the analog output continued to be a guarantee, but the parameters were more significant. Non-reference cards often did not reach the reference bars and this had a negative impact on performance.
The third point of success of the reference cards could be considered the Radeon 9800XT. It was basically the very first reference card, which came with a “large” (albeit single-slot) cooler, which, thanks to a larger diameter fan, did not have to increase the speed to the level of the then usual 40-45 mm frightened hornets. The acoustic performance of this solution was significantly more acceptable than small high-speed fans, which became unbearable after a year of operation. Attempts at custom solutions did not turn out better, so most manufacturers offered reference designs until the end of the card era. In connection with this card, it is worth mentioning that it was the first GPU to offer a manufacturer-guaranteed automatic overclocking (regulated by the core temperature), similar to today’s boost. The user had to turn on the feature in the drivers.
The fourth period of success of the AMD reference card was recorded with the Radeon X1950 XTX. The reference cooler blowing all the hot air out and equipped with a fan that didn’t rip your ears was basically new. Users and manufacturers had no general reason to address non-reference design. The situation was similar to the Radeon 9800XT.
You may remember other cases, but I personally no longer remember the situation where the reference design of the AMD high-end cooler would somehow excel – at best it did not lag far behind and at worst (which was later more common) there was no reason to prefer it with one exception, when connecting cards to CrossFire on motherboards that skip only one free between × 16 PCIe slots. Axial fan coolers, which could not develop greater static pressure, suffocated in contrast to the reference radial design, and the temperature of the top card rose dangerously.
A specific case was users who planned to use the card for a long time. Reference centrifugal coolers used to have better bearings, so they lasted longer without making all sorts of noise, which in some models increased the noise above the reference level over time.
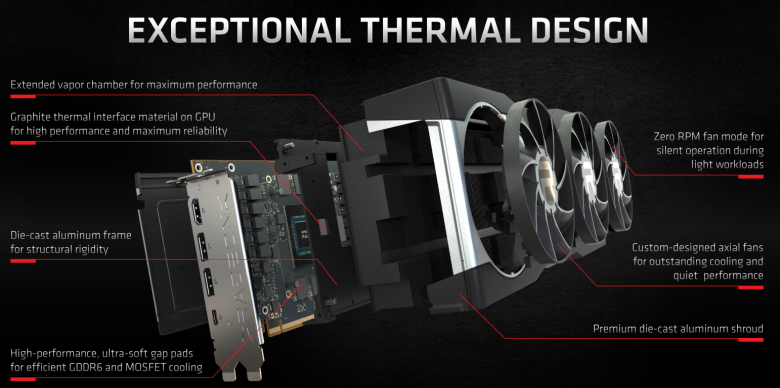
The Radeon RX 6800 XT is therefore the first solution after 14 years since the Radeon X1950 XTX, which is not only not a reason to criticize or reject, but which, according to a number of reviews, is better than Nvidia’s innovative “blowing” design. It is possible that non-reference cards with an even quieter heatsink will be available, but their dimensions will not be close to the standard size in which AMD managed to fit the heatsink and which can also accommodate ordinary cabinets.
The reason why AMD does not plan to continue producing reference cards may be the cost. The large vapor-chamber, which distributes all the heat from the core, is not a cheap affair and a cooler with heatpipes – albeit larger overall – is a cheaper alternative.
–