Atherosclerosis is a special type of arteriosclerosis, but the words are sometimes used interchangeably. Atherosclerosis evokes the accumulation of fats, cholesterol in the arterial walls, which can limit blood circulation. The plaque can burst, causing a blood clot. Although atherosclerosis is mostly thought of as a heart problem, it can affect arteries anywhere in the body. Atherosclerosis can be prevented.
What are the symptoms of atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis develops over time, it has no symptoms. You often won’t have symptoms of atherosclerosis until an artery is so narrowed that it can’t supply enough blood to organs and tissues. Occasionally, a blood clot completely blocks blood flow or even breaks open and can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
If you have atherosclerosis in the heart arteries, you may have symptoms, such as chest pain. If you have atherosclerosis in the arteries going to the brain, you may have signs such as numbness or weakness in your arms, trouble speaking, loss of vision in one eye, or loosening of the muscles in your face. These are the markers of a transient ischemic attack, which must be treated so as not to lead to a stroke.
If you are affected by atherosclerosis in the arteries in the arms and legs, you may have signs of peripheral arterial disease. If you have atherosclerosis in the arteries going to the kidneys, you develop high blood pressure or kidney failure.
When should you consult a doctor?
If you think you have atherosclerosis, do not hesitate to report it to a doctor. Also watch out for symptoms of strange blood flow, such as chest problems or leg pain. A diagnosis can prevent atherosclerosis from getting worse and prevent a heart attack or stroke. You should know that atherosclerosis is a disease that can begin in youth. Although the precise cause is poorly understood, atherosclerosis can begin with damage to the inner layer of an artery.
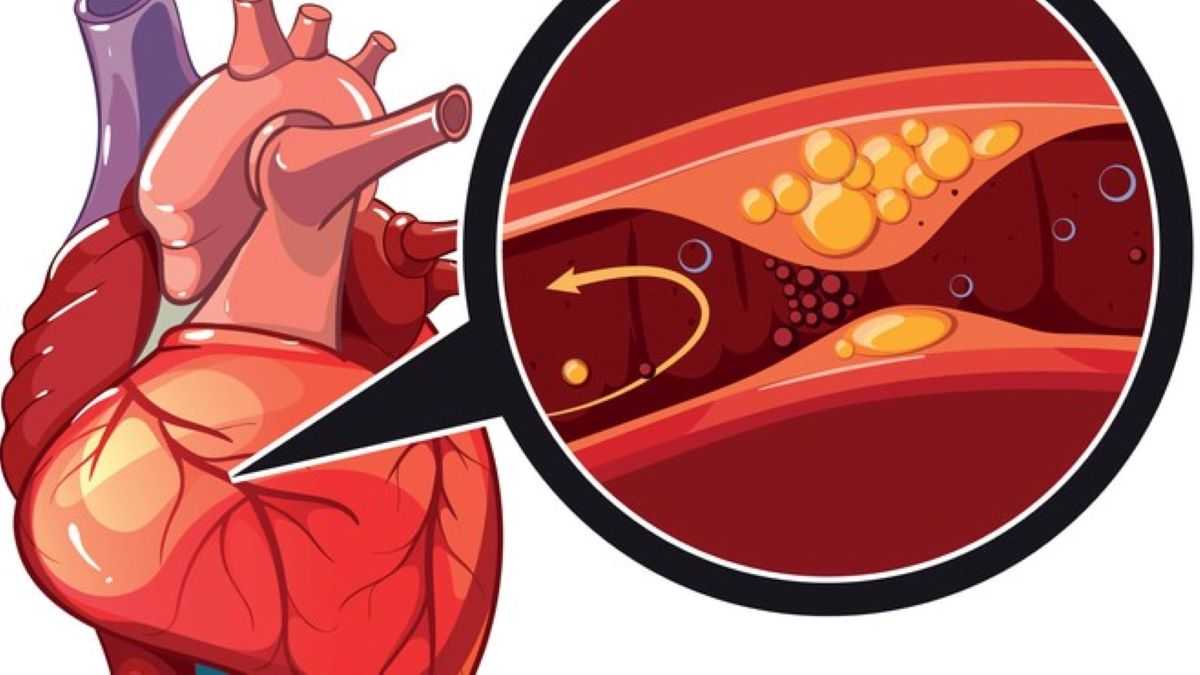
Once the inner lining of an artery is affected, cells and other substances clump together at the site of injury and collect in the inner lining of the artery.
Gradually, fatty deposits (made of cholesterol) also accumulate at the injury site and harden, clogging your arteries. The organs connected to the blocked arteries do not then receive enough blood to walk well.
In addition, the plaque lining can rupture, spilling cholesterol into the bloodstream. This can cause a blood clot, which can block the flow of blood to part of the body. A blood clot can also travel to other parts of the body, blocking the flow to another organ.
Complications of atherosclerosis are related to blocked arteries. When atherosclerosis narrows the arteries in your heart, you can develop coronary artery disease, which can cause chest pain, heart attack, or heart failure. When atherosclerosis narrows the arteries near your brain, you may have carotid artery disease, which can cause a transient ischemic attack.
When atherosclerosis narrows the arteries in the arm, you can develop circulation problems in your arms. This can make you less sensitive to temperatures, which increases the risk of burns.
Atherosclerosis can also cause cause aneurysms. It’s a bulge in the wall of your artery. There are few symptoms. If an aneurysm bursts, you can face internal bleeding which can be fatal. If a blood clot in an aneurysm becomes dislodged, it can block an artery at a distant point. To prevent diseases of this type, it is good to quit smoking, eat healthy foods, exercise often, maintain a healthy weight.
–

![The lunch and evening draw [EN LIGNE] The lunch and evening draw [EN LIGNE]](https://www.hommedumatch.fr/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/HeaderMobileKeno-1200x900-1.jpg)