[코로나19]First confirmation of’British mutant’ in Korea
Mutation occurs in G group, which is the largest epidemic in Korea, which has higher spreading power than existing S and V groups
Expert “Vaccine can be redesigned according to variations… Can’t rule out evolution as a variant virus”
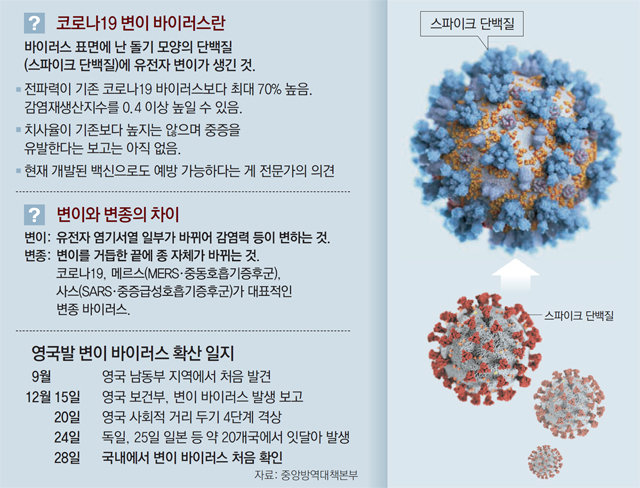
-The new coronavirus infection (Corona 19) mutant virus transmission power that was first confirmed in Korea on the 28th is known to be up to 1.7 times (70%) stronger than the existing virus. This means that the increase in confirmed cases could be 1.7 times faster than the present. However, experts believe that the mutant virus does not worsen the patient’s condition. In addition, it is analyzed that it can be prevented with the currently developed vaccine because it is in the stage of mutation, not a variant.
○ Transformation of Korea’s largest fashion group G
According to the quarantine authorities on the 28th, the mutant virus found in the UK and South Africa is a kind of group G, which has been the most prevalent at home and abroad since May this year. Although it is different from the existing virus genes in about 20 locations, it has the same protein structure as the G group virus. Ribonucleic acid (RNA) viruses, such as coronavirus, are often mutated due to their lack of corrective ability during the proliferation process. Kim Eun-jin, head of the Test Analysis Team 1 of the Central Defense Countermeasures Headquarters (Bang Dae-bon), explained, “As people change generations, viruses change little by little over generations.” “In RNA viruses, mutations are very common.”
 View larger
View larger-Experts analyze that some of the spike protein, which is a site that binds to cells in the body, may have increased its propagation power as mutations occur. Jeong Yong-seok, professor of biology at Kyung Hee University, said, “7 and 8 mutations were found in the presence of the spike protein. Among them, one or more mutations in the site that may be involved in binding to receptors in the body were identified.” However, it can be mutated by repeating mutations. Viruses in which pathogenicity, such as propagation power and toxicity, are significantly changed as the genetic information of the virus is greatly changed or the composition of important parts is changed, and it is called a variant virus. A prime example is the Zika virus, which caused fetal microcephaly in Brazil in 2016. Zika is a virus that has been discovered in Africa for decades. The Zika virus, which was prevalent in South America such as Brazil in 2016, has a much stronger pathogenicity than Africa and is classified as a variant virus.
○ The severity is low, but the transmission power is dangerous.
It is still unknown to what extent the mutant virus will affect the spread of coronavirus. To date, there has been no report of a rapid increase in the number of confirmed cases in countries where mutant viruses have been found. Professor Jeong Yong-seok said, “The spreading power of the G group is 9 to 10 times higher than that of the existing virus groups (S, V groups).” I said. There are many opinions that the severity will be similar to the existing virus. However, quarantine authorities have not ruled out the possibility of affecting the severity. Team leader Kim Eun-jin said, “Because the mutation occurred at the host cell binding site, there is a possibility that it may affect the antibody response or pathogenicity.” Experts see the likelihood that the mutant virus will neutralize the vaccine. “The latest vaccines are designed to be redesigned to match the virus mutation,” said Jeong Ki-seok, a professor of respiratory medicine at Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital. “It is unlikely that the vaccine will be disabled due to the mutant virus.”
But I can’t be relieved. This is because, as the spreading power increases, the number of confirmed cases increases, and as a result, the possibility of spreading the virus to high-risk groups such as the elderly increases. This means that the mortality rate can be high regardless of pathogenicity. Chun Eun-mi, a professor of respiratory internal medicine at Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital, pointed out that the increase in community infections increases the likelihood that the virus will flow into high-risk facilities such as nursing homes or hospitals, which will affect the mortality rate.
The possibility that the mutant virus will evolve into a mutant virus cannot be ruled out. Professor Nam Jae-hwan of the Department of Biotechnology at Catholic University stressed, “It is not a dangerous level yet, but it is like a rugby ball that does not know where the RNA virus will bounce, so we have to keep an eye on the mutation situation.”
Image [email protected]Go to reporter page>Reporter Kim So-min and Kim Seong-gyu
Copyright by dongA.com All rights reserved.
—
–


