No-Code, the digital trend that is committed to providing application development tools without relying on programming notions, has taken a great boost in recent years.
To exemplify the power of this creation modality, a developer presented a Twitter clone built under this mechanism.
The No-Code proposes to make available to developers who are not necessarily programmers, the possibility of building applications from scratch without even touching a line of code.
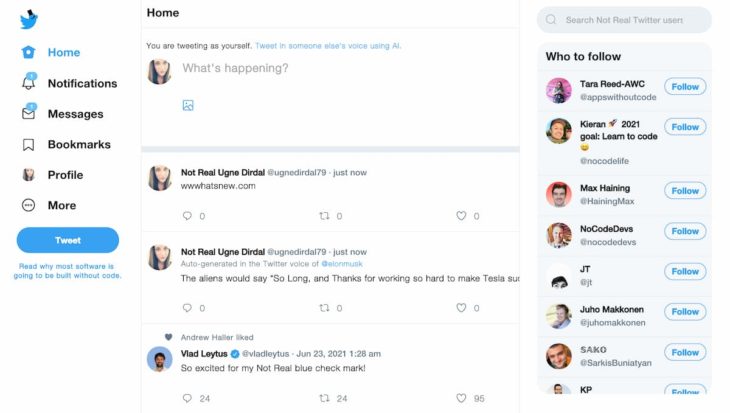
Looking at this from a distance, it may seem like a resource limited to creating basic applications, but practice shows us otherwise. A clear example is the commented application, Not Real Twitter.
As its name indicates, it is not the real Twitter, but it is a true copy, really very close, to the original social network, both in design and in functionalities.
To use this social network, it is possible to generate a profile automatically or by registering through the traditional route.
Within this platform, few differences can be noticed with the original. User accounts follow the same structure, as does the home section or the direct message mailbox. The application is fully functional and in a certain way, it gives us the illusion of being the Twitter of a parallel world.
A promising future for the No-Code
Six years ago, saw the light the first version of this clone, which can still be reviewed by following this link. Since then, a lot has changed and from the hand of Bubble, a tool used to create this application, it was demonstrated how far a project of this kind can go.
In a recent blog post, those responsible for this project commented on their vision about the potential of the No-Code. There they indicated that for newly emerging digital ventures, the hand of these tools has established a good ally to access complex resources, but of common use.
Taking as an example an application that emulates the dynamics of Airbnb, it is illustrated that using the No-Code resources already available, it is possible to create a catalog of properties, accompanied by a user registration system, reservations and payments integrated through processors external. Although, “behind the scenes” the application requires a complex portion of code, as they are common resources, they can be obtained in this way as easily added modules.
Although the possibilities are quite generous, they are not endless either. When a project grows naturally due to its activity, there are problems that are more difficult to attack with this class of resources, such as the integration of machine learning algorithms for content personalization or the technical optimization required to meet a large volume of simultaneous requests, as occurs in the case of real Twitter, for example.
Looking forward to the years to come, the AirDev team, creators of Not Real Twitter, commented that “Most software applications will be built using No-Code, while more complex applications will continue to be built with code”, relying on his diagnosis of the “easy” and “difficult” problems to attack.
This new concept of application development, despite not being a universal solution, has opened a new gateway to materialize digital projects.
– .