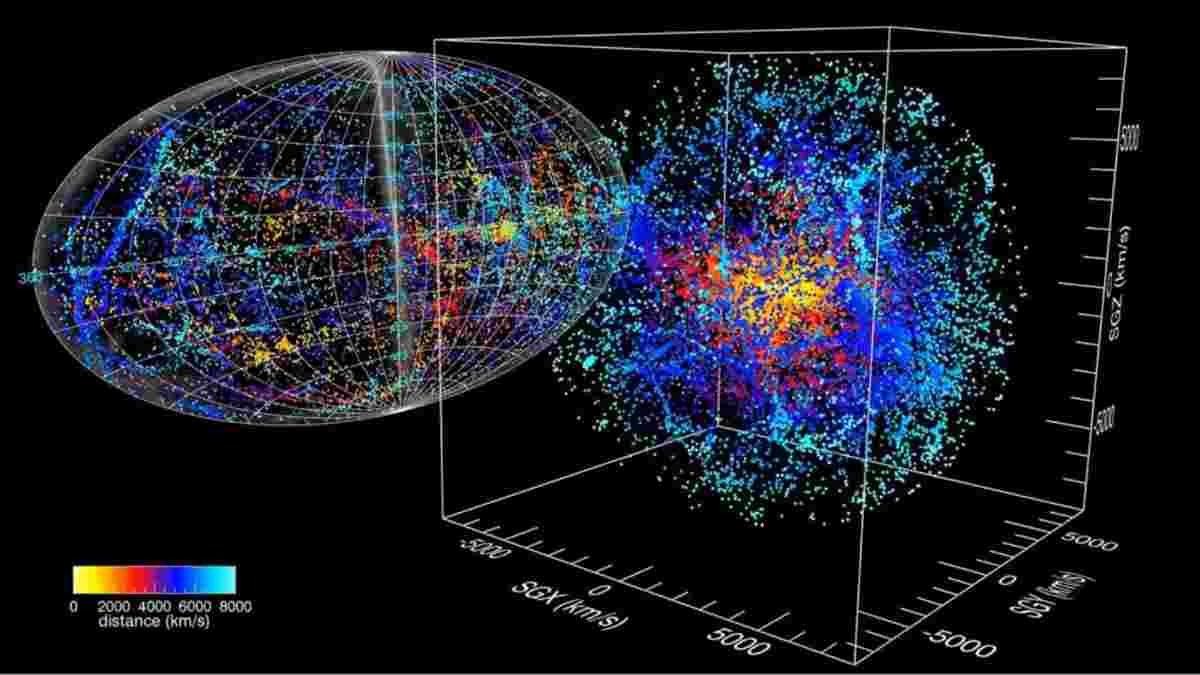
Universe Observables consist of various galaxies or matter that have been seen from Earth thanks to the light they emit.
We know that the universe is very wide with various constituent materials in it. Therefore, we cannot know all parts of the universe.
So far, there are several parts universe that humans have been able to observe from Earth. Matter in the universe that scientists have observed has light and other signals emitted.
Also read: The Difference Between Galaxy and Solar System, Don’t Be Fooled Again!
It finally made part of the universe known to man with the help of advanced tools. Even so, do you know how many regions of the universe have been identified?
Is Our Observable Universe Really Smaller?
About 13.8 billion years ago, the Big Bang started the cosmos. The universe is full of matter, antimatter, radiation, ultraheat states, and other solids.
After that, the volume of the universe would then expand and cool. You need to know that the current cosmic state is not only cold and swarming, but also contains gravitational forces and expands.
For thousands of years, humans on Earth have been trying to figure out how big our universe is. Unfortunately until now there is no definite picture.
But scientists have managed to observe some parts of the universe. These parts are certainly in accordance with the capabilities of sophisticated astronomical tools that humans have.
For the first time, scientists have updated the size of the observable universe’s radius. Apparently, the results are quite surprising because they are not as big as we thought.
In the latest measurements, it is known that the part of the universe that is technically visible from Earth is now shrinking by about 320 million light-years from all directions.
Physicists from the University of Sciences in Philadelphia, USA, Paul Halpern and Nick Tomasello used the latest data on the expansion of the universe. The data was collected from the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Planck spacecraft.
Also read: The Dimest Star Ever Identified, Here’s The List!
They found that the identified edge of the universe was actually 0.7% smaller than previously thought. With more accurate measurements, they managed to get the radius of the universe.
The radius of our universe is only 45.340,000 light years from the original 45.66 million light years. For additional information, 1 light year is equal to 9.5 trillion km.
“The difference of 320 million light-years may not be very significant on a cosmic scale, but it still makes our observable universe much smaller,” Tomasello said.
How to Calculate the Area of the Universe?
You may be wondering, how do scientists determine the area of the universe? At the stage of concrete calculations, scientists have an understanding of three things at once.
Here’s how to get a calculation of the size of the universe through three senses at once:
- How fast is the expansion of the cosmos happening right now. Scientists can measure its speed by a number of specific methods.
- Hot measure of universe At the moment. For their observations, scientists can use the cosmic microwave background thermal radiation.
- The composition that composes the universe. These include matter, radiation, neutrinos, dark matter, dark energy, antimatter, and so on.
Through these three things, scientists will be able to extrapolate back to the earliest stage of the universe, namely the time of the Big Bang which will determine the age and size of the universe simultaneously.
So far, it has been assumed that the universe is isotropic because the approximation of the distance to the end of the observable universe is the same in all directions. The word observed here is the extent to which humans see light.
At what distance will the light appear when the photons split during recombination. The detected gravitational waves indicate that it is now possible to detect non-light signals before the recombination period.
The best estimate for the age of the universe in 2015 is 13,799,021 billion years. Due to the expansion of the universe, humans observe objects that start out very close, but become far away more than a fixed distance of 13.8 billion light years.
Next, the scientists estimated the diameter universe observed at about 28.5 gigaparsecs or 93 billion light years with the end of the universe 45.34 billion light years at the most recent calculations. (R10/HR-Online)
–