[우리문화신문=유용우 한의사] A cold is an appearance in which an external fraud (evil qi, virus) invades and the body’s defenses are exposed. Since most colds progress as airborne contaminants enter the respiratory tract, most symptoms appear from the nose. The primary gateway to defend against the invading virus is the adenoids, which we call the tonsils. Therefore, when the virus is rampant in the process from the entrance of the nose to the adenoids, the runny nose often increases, showing symptoms of a cold and starting a cold, which is also called acute rhinitis.
Usually, if we defeat the invasion of the virus early and lightly with the defense action of adenoids, there is no burden or change in our body. If the symptoms that appear when you catch a cold are not too severe and are cleared up within 3 days, the cold will end as a passing phenomenon. However, if the severity of the cold is severe and it progresses for more than 3 days and symptoms are revealed beyond the adenoids, various physiological phenomena are changed and various symptoms are revealed as the body’s defense system is overloaded. From this point on, it becomes a disease rather than a symptom of a cold.
1. Acute sinusitis
The typical symptoms are pain and pressure in the face, runny nose, nasal congestion, and the like. When a runny nose or stuffy nose continues due to a cold, the mucous membrane of the nose swells and inflammation progresses. In addition, as the passage of the turbinate leading to the sinuses is narrowed, the discharge of the sinuses is obstructed.
Symptoms that appear during upper respiratory infection include nasal congestion, nasal discharge (runny nose), fever, malaise, and drowsiness. In severe cases, it may be accompanied by tenderness in the face and headache. When pus forms, it flows down the nose, and some goes from the nose to the back of the throat, and when it is spit out, the pus may turn yellow or green. If your nose is blocked, you may not be able to smell, or you may have a strange smell. In some cases, the patient complains of coughing without any other symptoms.
2. Acute pharyngitis
The typical symptom is a severe cold condition in which foreign body sensation in the throat, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), and pain appear. Inflammation of the pharynx caused by a viral or bacterial infection is called pharyngitis. It is mainly caused by fatigue and overwork, heat-related illnesses, excessive temperature differences, and diseases that reduce constitutional weakness and immune resistance.
 photo”/>
photo”/>
Pharyngitis is most often caused by a bacterial, viral or rarely fungal infection. It can also be caused by excessive smoking, drinking, overwork and dehydration. In addition, it is caused by inhalation of irritating substances or vapors, and the spread of inflammation in the adjacent area.
In the early stages, symptoms such as a foreign body sensation in the pharynx, dryness, and mild coughing appear, and as it worsens, pain, difficulty swallowing (difficulty swallowing food), high fever, headache, general malaise, and anorexia are reported. In addition, there is a smell from the mouth, tongue sticking to the tongue, pain under the ear, and in severe cases, the lymph glands (lymph nodes) in the neck may swell or complain of pain. In particular, a lot of pharyngitis symptoms were revealed in the last corona variant and this spring’s cold.
3. Acute laryngitis and tracheitis
The main symptom is a coughing cough and is a cold disease that requires quick treatment. Acute laryngitis is caused by an infection such as a virus or bacteria, and is an inflamed condition in the larynx and surrounding tissues. It often appears as a partial symptom of a cold, and most of them are accompanied by a cold (acute rhinitis) or pharyngitis, coughing occurs, and voice changes.
In most cases, the larynx itself is inflamed due to infectious diseases caused by viruses and bacteria, or inflammation of surrounding tissues such as pharyngitis and tonsillitis spreads to the larynx.
In general, foreign body sensation or pain occurs in the pharynx when food or saliva is swallowed. When coughing, it makes a distinctive sound. If acute laryngitis is left untreated, inflammation progresses to surrounding tissues such as the pharynx, tonsils, nasal cavity, and bronchi, resulting in symptoms such as coughing, phlegm, runny nose, and nasal congestion. In addition, the voice may change and vocalization may be difficult, and it may be accompanied by systemic symptoms such as fever and muscle pain.
4. Acute bronchiolitis in children
The main symptom is labored breathing. It appears when the symptoms of a cold get worse and spread to the bronchioles.
Acute bronchiolitis is a disease caused by inflammatory obstruction of the small airways and is a common lower respiratory disease in infants. It usually occurs before the age of 2 years, but it is most common in the age of 6 months. It is a common disease among hospitalized infants in many regions.
Symptoms of bronchiolitis are initially a mild upper respiratory infection accompanied by a clear runny nose or sneezing. After these symptoms continue for several days, high fever (38.5 ~ 39 ℃) occurs and appetite decreases. Then, symptoms such as wheezing, wheezing cough, shortness of breath, and respiratory instability gradually appear. Feeding can also be difficult as breathing speeds up and there is not enough time to suck or swallow milk.
In mild cases, symptoms disappear within 1 to 3 days, but in severe cases, symptoms appear within a few hours and last for a long time. When severe disorders occur, the respiratory rate reaches 60 to 80 times per minute, and severe air shortage and cyanosis (appearing blue due to reduced oxygen supply to parts such as lips, fingertips, ears, and mucous membranes) appear. Flaring of alae nasi, indentation between the ribs or lower part of the ribs.
Your exhalation becomes longer, and you may hear a ‘wheeze’ or ‘grunt’ breath sound. In very severe cases, capillary bronchial obstruction occurs almost completely, and breath sounds are barely audible. It is often accompanied by diarrhea in the terminal stage, and the elasticity of the bronchioles decreases, leaving sequelae in which the overall metabolic function deteriorates.
5. Acute otitis media
Typical symptoms are fever, ear pain, and severe nasal congestion, which are secondary diseases of the common cold. If the cold continues and the mucous membrane in the nose swells, the nose cannot actively cope with the change in air pressure. If the function of the middle ear (middle ear) and the air tube that ventilates the middle ear (the tube that connects the middle ear and the pharynx) is not functioning well, or viruses or bacteria invade through the ear tube and adhere to the mucous membrane, causing inflammation, resulting in inflammation. Otitis media occurs when pathological changes occur in the middle ear mucosa.
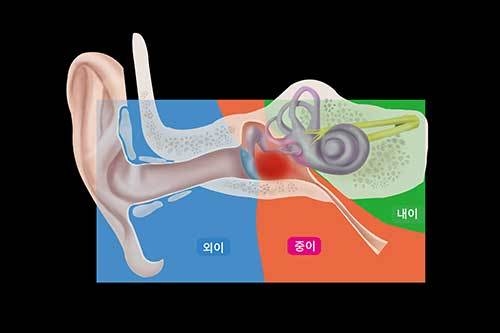
In acute otitis media, various general inflammatory symptoms such as fever, headache, vomiting, diarrhea, indigestion, anorexia, lethargy, anxiety, and nervousness appear gradually or suddenly depending on the severity of the inflammatory condition or the symptoms of the disease. It may be accompanied by acute symptoms of the ear, such as fever, ear pain, hearing loss, tinnitus, and otorrhea (a disease in which pus comes out of the ear). In the case of otitis media with effusion, acute symptoms disappear, but conductive hearing loss with ringing in the ears, a feeling of fullness in the ears, and magnetic coelucia with loud echoes of one’s own voice appear.
