CSIA surveillance – The report with 2023 data
In November 2023, the Istituto Superiore di Sanità (ISS) published the report with the 2023 data from the National Surveillance of the Consumption of Hydroalcoholic Solution (CSIA) for hand hygiene in hospitals, established in our country in 2021.
In Italy, the surveillance of the consumption of hydroalcoholic solution (CSIA) for hand hygiene was established in 2021 and its importance was underlined as a priority by the National Plan to combat Antibiotic Resistance (PNCAR) 2022-2025 and from the National Prevention Plan 2020-2025. The objective of surveillance is to monitor over time, at national and regional level, the consumption of hydroalcoholic solution in hospital settings, in every public hospital for acute care, but also in affiliated and non-affiliated private facilities and in social-welfare and social-health facilities if equipped with a ministerial code, as long as they have days of hospitalization. At a central level, the management of CSIA surveillance is the responsibility of the Department of Epidemiology, Biostatistics and Mathematical Models of the Infectious Diseases Department of the ISS. Each Region/Autonomous Province (PA) identifies a contact person for CSIA surveillance. Each healthcare facility in the area has a facility contact person, responsible for collecting and sending data via the web platform
https://csia.iss.it/.
The WHO suggests expressing the consumption of hydroalcoholic solution in liters of solution consumed every 1000 Days of Ordinary Hospitalization (L/1000 GDO) and indicates an average consumption of 20 L/1000 GDO as the reference standard. The consumption data were collected on three levels: entire structure (level I), hospitalization area (level II) and broken down by individual areas/disciplines of care (Medical, Surgical, Intensive Care, Orthopedic Traumatology, other hospitalization areas , level III).
The main Italian data for 2023 and the 2020-2023 trend
In Italy, in 2023, data relating to the consumption of hydroalcoholic solution for hand hygiene in hospitals were provided by a total of 690 facilities in 20 Regions/PAs, observing a gradual increase from 2020.
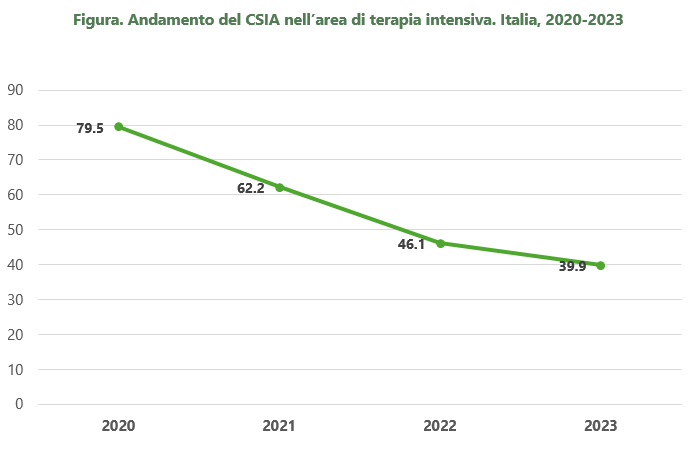
The national median consumption of hydroalcoholic solution in 2023 for the entire facility was 17.2 L/1000 GDO, 11.7 L/1000 GDO for ordinary hospitalization, 9.6 L/1000 GDO for the medical area , 11.0 L/1000 GDO for the surgical area, 39.9 L/1000 GDO for the intensive care area and 8.9 L/1000 GDO for the orthopedic area.
Considering only ordinary hospitalization, a progressive decline in CSIA was noted: in 2020 and 2021 the median consumption of hydroalcoholic solution was higher than the threshold of 20 L/1000 GDO, 24.5 L/1000 GDO and 20.4 L respectively /1000 GDO, while in 2022 and 2023 it was below the threshold (15.6 respectively L/1000 GDO and 11.7 L/1000 GDO).
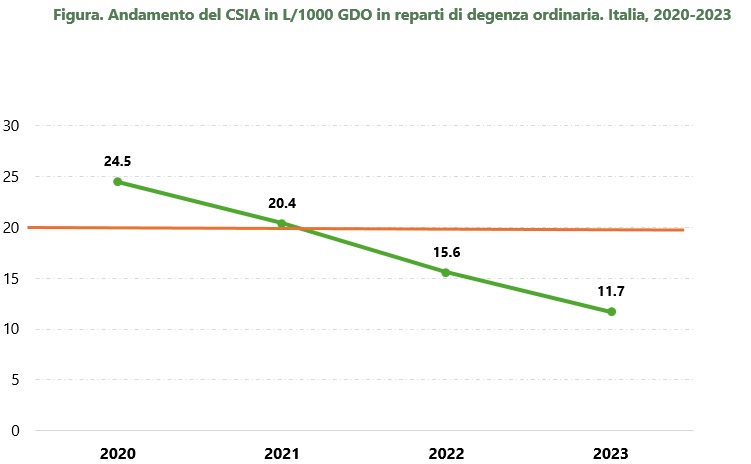
The orange line indicates the reference standard of average consumption of hydroalcoholic solution of 20 L/1000 GDO established by the WHO
The PAs of Bolzano and Trento stand out for the highest consumption in almost all areas, other regions, especially in southern Italy, show lower consumption.
The median consumption of hydroalcoholic solution at a national level in both the medical and surgical areas was 20.3 and 23.8 L/1000 GDO respectively in 2020, while it was lower in 2021, 2022 and 2023.
In intensive care, it remains high, however with a progressive decline from 2020 to 2023 and with a value lower than the European average of 92.2 L/1000 GDO in 2022.

**What are the potential implications of the observed decrease in CSIA consumption for infection control in Italian hospitals, considering the ongoing importance of hand hygiene?**
## Interview: Understanding Hand Hygiene Trends in Italy – A Discussion with Dr. [Expert Name]
**Introduction:**
Following the release of the 2023 data report on hydroalcoholic solution consumption (CSIA) for hand hygiene in Italian hospitals by the Istituto Superiore di Sanità (ISS), World Today News spoke with Dr. [Expert Name], [Expert title and affiliation] , to analyze the trends and implications of these findings.
**World Today News:** Dr. [Expert Name], thank you for joining us. The ISS report highlights a gradual decrease in CSIA consumption since 2020. Can you elaborate on this trend and what factors might be contributing to it?
**Dr. [Expert Name]:** Certainly. The decrease in CSIA consumption, especially in ordinary hospitalization areas, is an interesting development. While the 2023 median consumption of 11.7 L/1000 GDO is still below the WHO’s recommended threshold of 20 L/1000 GDO, it represents a significant shift from 2020 and 2021 when consumption was considerably higher.
Several factors could be at play here. Firstly, we have witnessed a reduction in COVID-19 cases, leading to potentially less stringent hand hygiene protocols in some settings. Secondly, increased awareness and training on appropriate hand hygiene practices could have contributed to more efficient utilization of hydroalcoholic solutions. it’s possible that individual facilities are implementing targeted strategies to optimize their consumption rates.
**World Today News:** The report also shows variations in CSIA consumption across different areas within hospitals. For instance, intensive care units showcase significantly higher consumption compared to orthopedic areas. What might explain these disparities?
**Dr. [Expert Name]:** This is to be expected. The intensity of patient care and the nature of medical procedures significantly influence hand hygiene practices. Intensive care units, with their critically ill patients and more invasive procedures, necessitate a higher frequency of hand disinfection. Conversely, orthopedic wards, with their focus on musculoskeletal issues, likely involve less complex interventions.
**World Today News:** Looking ahead, what are the key takeaways from this report and what further actions are required to ensure effective hand hygiene practices in Italian healthcare settings?
**Dr. [Expert Name]:** This report underscores the importance of continued surveillance and monitoring of CSIA consumption.
It’s crucial to maintain awareness and adherence to best practices, reviewing and adapting protocols as needed. Encouraging ongoing training and education for healthcare workers, promoting research on optimizing hand hygiene techniques, and exploring new, sustainable sanitization solutions are all vital steps forward.
Furthermore, we need to ensure equitable access to these resources across all healthcare facilities, regardless of their size or location.
Thank you, Dr. [Expert Name], for your valuable insights. This data provides crucial information for ensuring the continued health and safety of patients and healthcare workers in Italy.

