lower electricity bill at the end of the year? Your TV can help with this. (Image: corvalola, Avector Krakenimages.com – adobe.stock.com)”/>
Do you want a lower electricity bill at the end of the year? Your TV can help with this. (Image: corvalola, Avector Krakenimages.com – adobe.stock.com)
How much electricity and money does a television like this actually use per year? This depends on factors such as screen technology, size, age or length of use.
We have calculated this using an example. Anker writes that a 65-inch device consumes an average of 94.7 watts during operation. We have this with the following values Blitzrechner hunted:
- Performance: 95 Watt
- Frequency of use: daily
- Duration of use: 4 hours
- Consumption in standby: 2 Watt
- Electricity costs: 53.30 cents per kilowatt hour
The result: The annual consumption of a 65-inch television is 153.30 kWh (14.60 kWh of which is in standby). This translates into a total of 81.71 euros per year.
This number can be changed with our 5 tips.
5 ways to save electricity on your TV
Disclaimer: In this article we subordinate everything to the energy saving aspect. So there is no focus on image quality. Modern televisions are already not so power hungry; So you won’t save horrendous sums. As we all know, small animals also make a lot of mess.
Reduce brightness

In dark rooms, many TVs automatically dim the picture and this saves electricity. (Image: HelenP – adobe.stock.com)
A brighter image also means more power consumption, logically because more energy is required. Accordingly, it is worth turning down the brightness parameter of your television.
There is two good news for owners of modern TVs:
- Automatic light sensors dim the image when the room is dark.
- The cinema mode is actually set quite dark. Using the preset does not affect the image quality.
If your living room is quite bright, for example with lots of windows, close the curtains instead of increasing the brightness on the TV. Your wallet will thank you.
Use sleep timer
I’m sure it happens to all of us: we turn on the TV and after 30 minutes at the latest we’re asleep on the couch – while the TV is still running.
There is a built-in solution for this: Many devices have a sleep timer that automatically switches off the TV after a certain number of hours. For example, on Samsung TVs, this setting is under the Eco options:
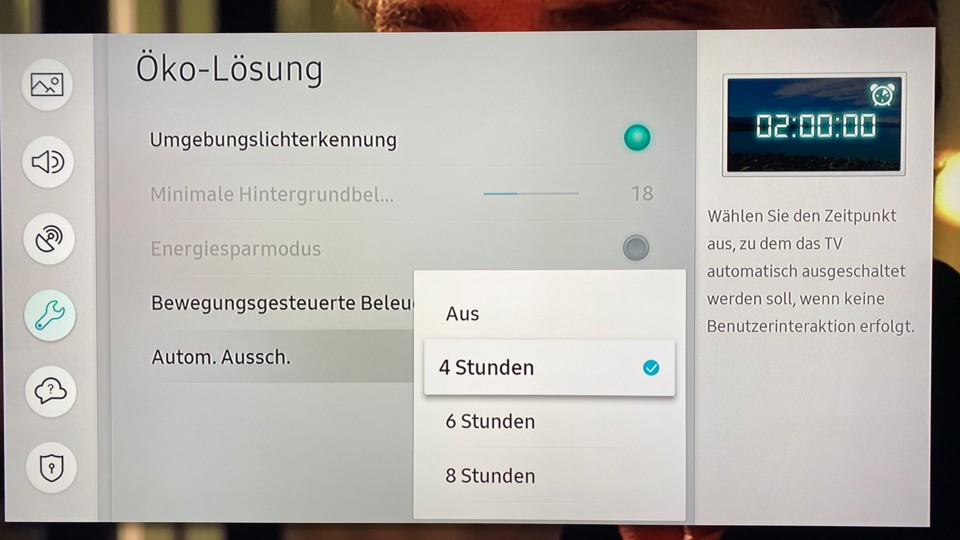
With this model you can choose between 4, 6 and 8 hours for the sleep timer.
Turn off screen
Many people leave the television on so that something is happening in the background. Others use music streaming services on the TV. Theoretically, if no one is looking, you don’t need a picture.
Most devices have a function that allows you to turn off the screen while the TV continues to run. Since the display consumes the most power (especially in large models), this is particularly worthwhile. Alternatively, you can also set the brightness to a minimum.
Unplug the TV
Admittedly, standby mode really doesn’t use all that much power. In the calculation example from the receipt of the article, that is at least 7.78 euros per year. You can save this by unplugging your TV when you’re not using it – and it boosts performance.
Be careful with OLED TVs! In standby mode, they often run a routine that cleans the organic pixels. Interrupting the television or regularly pausing the cleaning programs can damage the display in the long term. It’s best to use a timer that turns off the TV after an hour or at night.
Avoid HDR
The tip is only for hard-core savers: Turn off HDR if you want to save power. In order for the contrast expansion to really score, the device has to deliver a lot of power – and that costs money. That’s why the EU energy labels for TVs also indicate the power consumption during HDR operation.
![]()
![]()
There are a few more rules of thumb regarding the power consumption of televisions:
- Newer devices generally use less power than old ones.
- Screen size affects power consumption: the larger, the higher the consumption.
- OLED is considered the most energy efficient panel technology because it has no backlight, but LCDs typically do not use significantly more power.

