Astronomers have discovered that comet C/2024 L5 (ATLAS) will be thrown out of the solar system forever. After a close orbit of Saturn in 2022
This comet was first discovered on June 14, 2024, by the Project ATLAS asteroid tracking system, or the Terrestrial Asteroid Impact Last Warning System, which is the same system that co-discovered asteroid C/2023 A3 or Comet Zijin that is currently visible in the early evening sky
By observing the position of comet C/2024 L5 a total of 142 times, astronomers discovered that the comet has a hyperbolic orbit. Or will it exit the solar system forever? After passing closest to the Sun on March 10, 2025, at a distance of about 513 million kilometers.
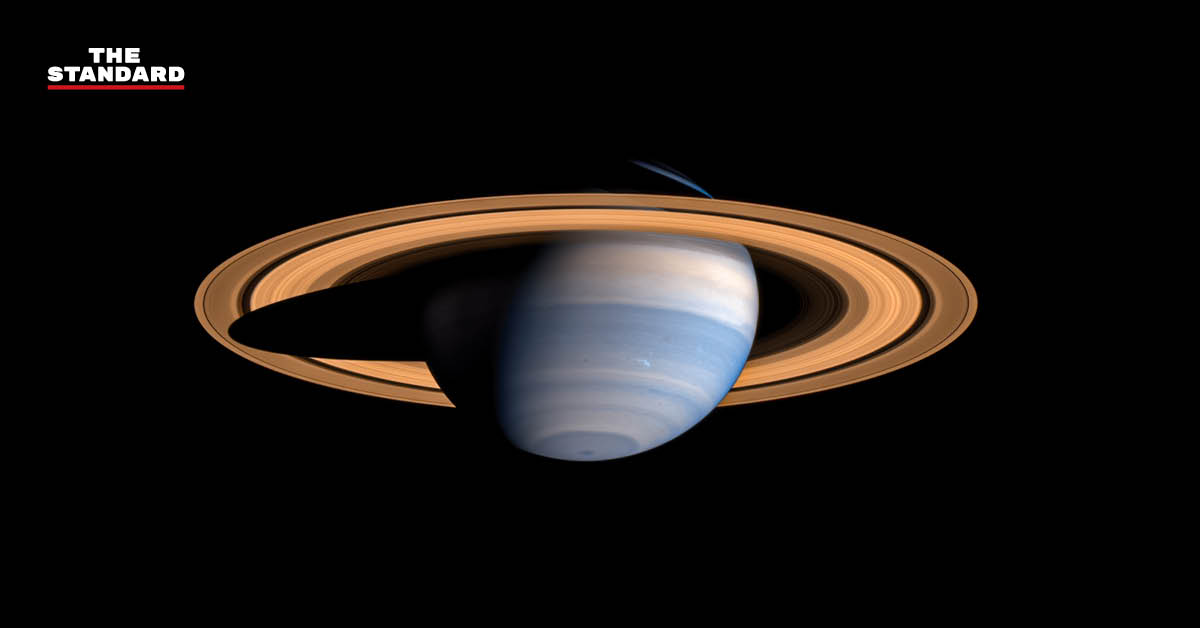
However, astronomers discovered that this comet was in a very close orbit to Saturn on January 24, 2022, at a distance of about 392,000 kilometers, or close to the Earth-Moon distance. This caused the gas planet’s gravitational pull to affect its orbit, causing C/2024 L5 to be ejected from the solar system forever, following in the footsteps of comet C/1980 E1 (Bowell), whose close approach to Jupiter was eventually ejected from the solar system.
Although comets of extrasolar origin have been discovered, including comets 1I/ʻOumuamua and 2I/Borisov, which were visitors from beyond the boundaries of the solar system. and passed through our star system over time Before you leave and never return Instead, astronomers suspect that comet C / 2024 L5 came from the solar system and was sent to out after him.
Comet C/2024 L5 (ATLAS) cannot be seen with the naked eye from Earth. Although it is expected to approach the Sun in early 2025, it is still 3.4 astronomical units away from the Sun, or 3.4 times the distance between Earth and the Sun. and will move at a speed of 2.8 kilometers per second During its journey to interstellar space (Voyager 1 travels at a speed of 16.9995 kilometers per second).
picture: JPL-Caltech / SSI / CYCLOPS / Kevin M. Gill / NASA
reference:

![What outrageous talent do you honestly want to see come back? 3rd place Ryoko Hirosue, 2nd place Yuya Tegoshi, overtaking 1st place with some saying “Nobody replaces me”[Faighnich dha 500 neach]- Smart FLASH/Smafura[光文社週刊誌] What outrageous talent do you honestly want to see come back? 3rd place Ryoko Hirosue, 2nd place Yuya Tegoshi, overtaking 1st place with some saying “Nobody replaces me”[Faighnich dha 500 neach]- Smart FLASH/Smafura[光文社週刊誌]](https://data.smart-flash.jp/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/23180823/hirosue_ryouko2_thumb.jpg)