The African Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is expected to announce soon whether it will classify smallpox, or what the World Health Organization has called smallpox, as a global public health emergency. -land, due to its rapid spread in central and eastern Africa.
The current monkeypox outbreak is more worrying this time than previous incidents because it involves a new variant of the disease, which experts say is so mutated that they have ever seen.
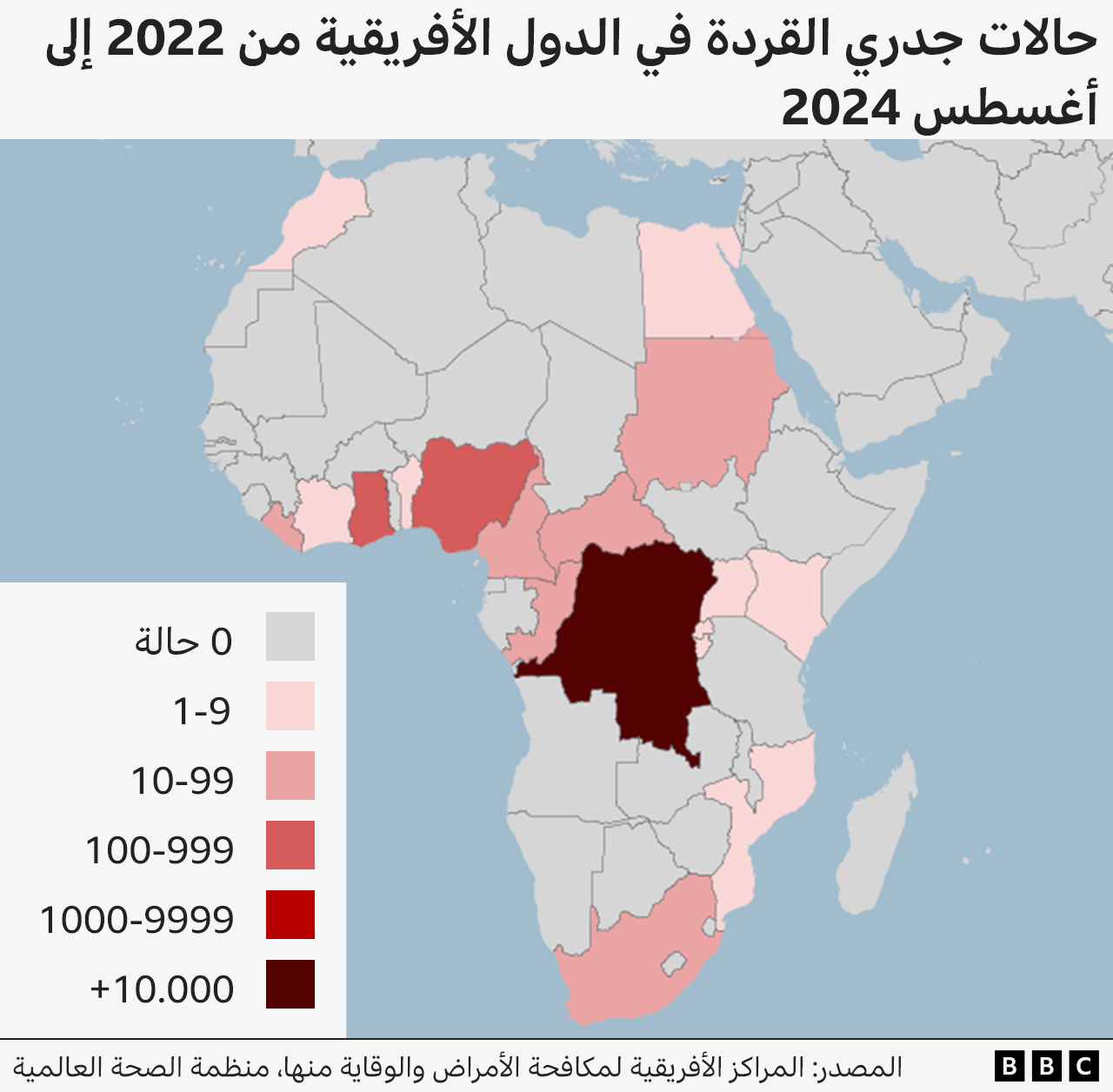
How common is mottled and in which countries does it occur?
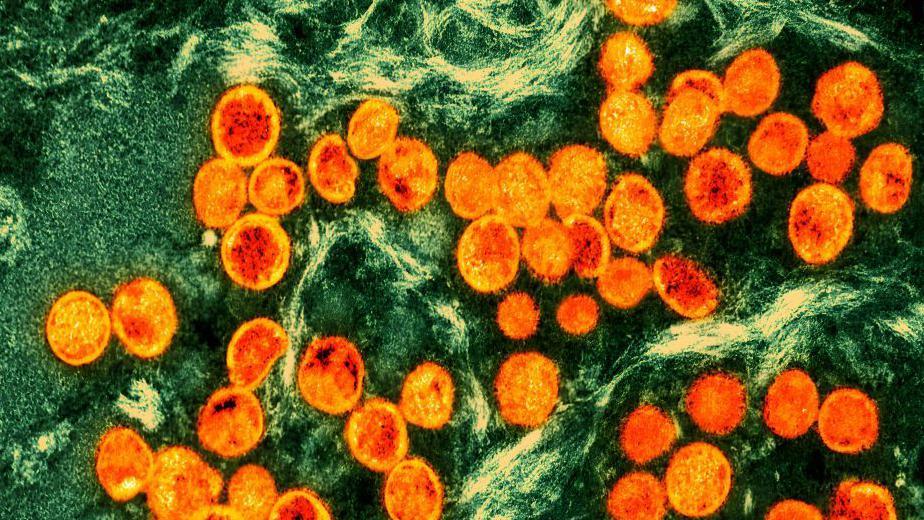
Smallpox is caused by the smallpox virus. It belongs to the same group of viruses that cause smallpox (but it is much less harmful).
The virus was originally transmitted from animals to humans, but is now transmitted between humans.
It is more common in remote villages in the tropical rainforests of Africa, in countries such as the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
In these areas, there are thousands of cases and hundreds of deaths from the disease every year – with children under the age of 15 being worst affected.
There are two main types of the virus circulating.
“Division I” is endemic in Central Africa. This “class” is the new, stronger type of virus involved in the current outbreak.
The Africa Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says there were more than 14,500 cases of monkeypox and more than 450 deaths from it between the beginning of 2024 and the end of July. This represents a 160 percent increase in infections and a 19 percent increase in deaths compared to the same period in 2023.
While 96 percent of mosaic cases occur in the Democratic Republic of Congo, the disease is spreading to several neighboring countries, such as Burundi, Kenya, Rwanda and Uganda – where it is not as usually endemic.
A milder strain of monkeypox known as Clade 2, found in West Africa, will cause a global outbreak in 2022.
The disease has spread to nearly 100 countries, including countries in Europe and Asia, which do not normally see the virus, but have controlled it by vaccinating vulnerable groups.
There is poor access to monkeypox vaccines and treatments in the Democratic Republic of Congo, and health officials are concerned about the spread of the disease.
What are the symptoms of the disease?
Initial symptoms include fever, headache, swelling, back pain, and muscle pain.
Once the temperature drops, a rash can appear, often starting on the face and then spreading to other parts of the body.
The rash, which can be very itchy or painful, changes and goes through different stages before it turns into a crust, which later falls off. Wounds can cause scarring.
The disease usually goes away by itself and lasts from 14 to 21 days.
In severe cases, lesions can attack the whole body, especially the mouth, eyes, and genitals.

How does the disease spread?
Mumps spreads from person to person through close contact with an infected person – such as through sex, skin-to-skin contact, and talking or breathing close to another person.
The virus can enter the body through infected skin, the respiratory system, or through the eyes, nose or mouth.
It can also be spread by touching objects contaminated with the virus, such as bedding, clothes and towels.
Another method is close contact with infected animals, such as monkeys, rats, and squirrels.
During the global outbreak in 2022, the spread of the virus was mainly through sexual contact.
The current outbreak in the Democratic Republic of Congo is caused by sexual contact, but it has also been found in other communities.
Who is most at risk of infection?
Most cases are found in sexually active people and men who have sex with men. People who have many new sexual partners may be at increased risk.
Anyone who is in close contact with a person with symptoms, including health workers and family members, can catch the virus.
The advice is to avoid close contact with anyone who has monkeypox, and to wash your hands with soap and water if you have the virus in your community.
Those infected must isolate themselves from others until their wounds disappear.
The World Health Organization says condoms should be used as a precaution when having sex for 12 weeks after recovery.
How will it be treated?
A drug designed to treat smallpox may also be useful in treating smallpox, but research into its effectiveness is still limited.
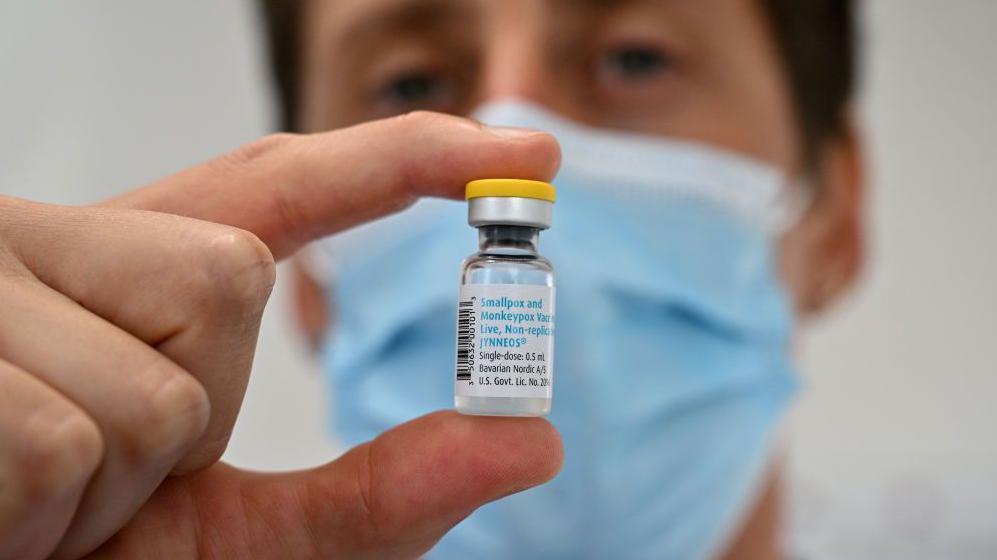
Outbreaks can be controlled by preventing disease – and vaccines are the best way to do this.
There are three vaccines, but only people who are at risk, or who have been in close contact with an infected person, can receive them.
The World Health Organization does not currently recommend vaccinating the entire population.
More trials of vaccines against new strains of monkeypox are needed to understand how much protection they provide.
The World Health Organization recently asked drug manufacturers to release their monkeypox vaccines for emergency use, even though there is no official approval for these vaccines in the countries that need them.
2024-08-13 21:30:05
#Monkeypox #spread #Cedar #News

