We continued at
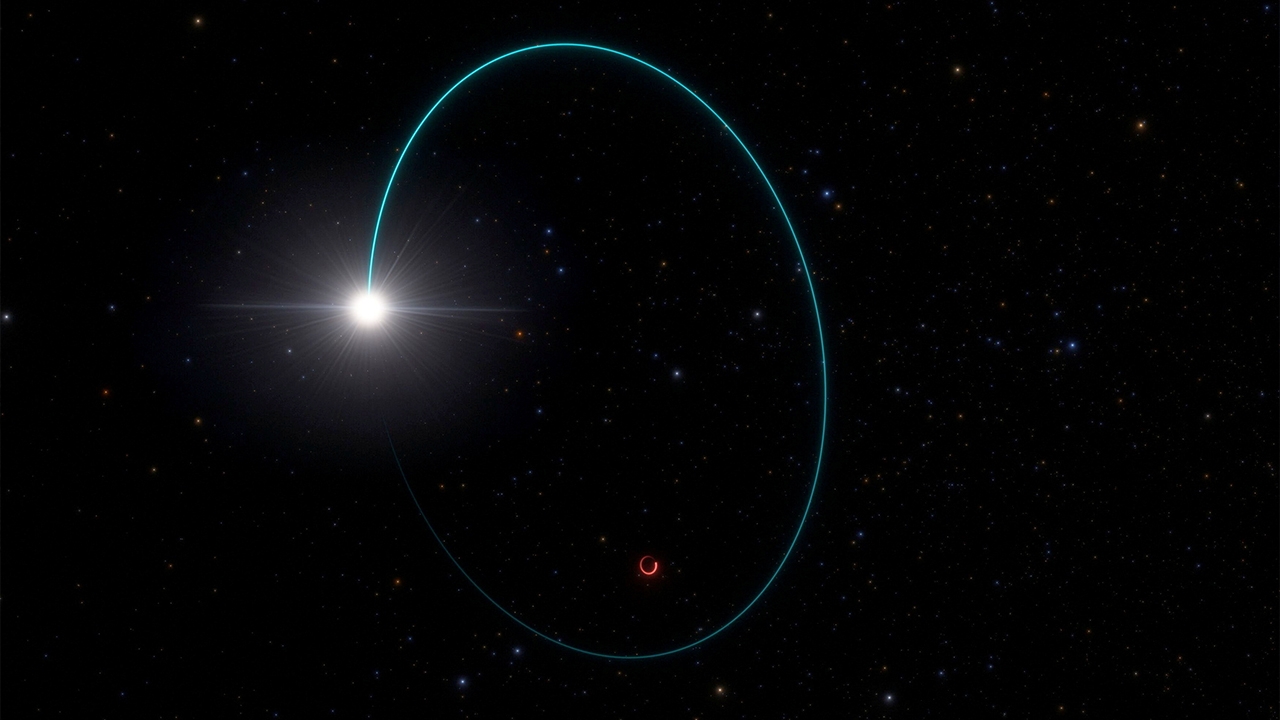
Black holes are extremely dense objects. Gravity is so strong that even light cannot escape. This makes them difficult to see. But today’s devices can overcome it. It allows us to know where there are black holes in the universe, especially in the center of our own Milky Way galaxy. characterized as a supermassive black hole. (super black hole) named Sagittarius A* or Sgr A* resides in this supermassive black hole 4 million times larger than the Sun and is about 26,000 light years from Earth.
But recently the research team was led by engineers from the French National Center for Scientific Research. Working at the Paris Observatory Seen on the European Space Agency’s Gaia spacecraft mission. along with data from the European Southern Sky Observatory’s Very Large Telescope and other ground-based observatories Report on the discovery of the largest black hole in the Milky Way galaxy. Named Gaia BH3, it has a mass 33 times that of the Sun. The team revealed that Gaia BH3 was accidentally discovered in the constellation Eagle. And this supermassive black hole was created after the explosion of a star just 2,000 light years from Earth.

The research team concluded that Gaia BH3 is a black hole that may have formed after the death of a star with a mass more than 40 times the mass of the Sun. Black holes form when a star collapses and are therefore called stellar black holes. It is also the second closest black hole to us discovered so far.