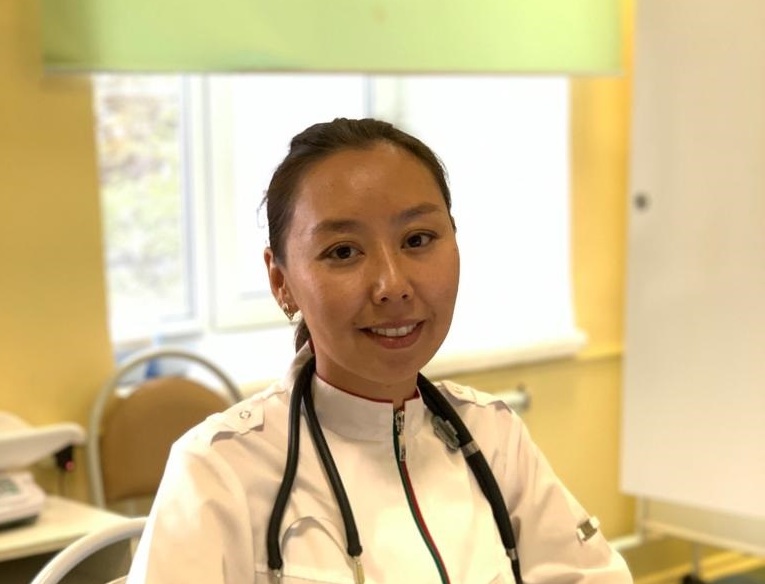
Pediatrician Maria Petrova: “Children, and adults too, do not get colds because of drafts.”
Any cold is caused by viruses that live around us and are activated during the transition period – from autumn to winter and from winter to spring. Today’s weather, with its unexpected changes in warmth and cold, may well provoke a cold. Listening to the advice of “experienced” mothers and grandmothers, we follow myths and miss the onset of illness in children. To prevent this from happening, the pediatrician of the capital’s Children’s Infectious Diseases Clinical Hospital, Maria Petrova, debunks the myths.
Myth one: the child has a “common” cold (ARVI), a doctor’s examination is not necessary.
M.P. Indeed, in many cases, consulting a doctor is not necessary, but there are a number of symptoms that should alert the parent and become a reason to visit a specialist: the child has a high body temperature for a long time or has reappeared, a strong or paroxysmal cough, difficulty breathing, weakness, ear pain. By the way, not all mothers know how to distinguish the flu and that there is effective antiviral therapy, which must be started in the first two days after the onset of symptoms. If a child is sick, it is very important to create a calm environment for the sick child and protect his sleep, especially at elevated body temperatures. Ventilate the room several times a day, remove dust from furniture and floors, and do wet cleaning. The patient’s bed should be clean, blankets and sheets should be shaken off, pillows should be fluffed. Underwear should also be clean and dry. It is necessary to monitor the cleanliness of the skin, you need to wash and bathe the child. If a child has a decreased appetite, then food is given to him in small portions. There is no need to force feed him; it is better to give him boiled water as often as possible.
Myth two: the child has a high fever and needs an antibiotic.
M.P. Cold and flu viruses cannot be treated with antibiotics. At the same time, if a person takes antibiotics unreasonably, bacterial resistance to these drugs develops. And at the moment when the antibiotic is really needed, it may not work.
Attention!
At high temperatures, more often in young children, febrile convulsions may occur. In this case, the child must be laid on a flat surface and any damaging objects removed. Unbutton tight clothing (to make breathing easier). Carry out emergency prevention of tongue biting during convulsions: to do this, turn your head to the side, you can turn your whole body. Place a twisted scarf, bandage, or cotton wool between the molars to prevent biting the tongue or cheek. And immediately call an ambulance. If the convulsions have stopped, but the body temperature remains high, give antipyretic drugs recommended by the pediatrician.
Myth three: the child has a cold, close the windows and limit walks.
M.P. Children, and adults too, do not get colds because of drafts. In the vast majority of cases, the cause is a virus. This means that you need to regularly ventilate the room, let in fresh air to clean it of viruses. The temperature in the room should be between 18-22 degrees. Don’t forget about hardening procedures, they increase the body’s resistance to influenza and acute respiratory infections. Local hardening methods include gargling with cool water, walking barefoot on the floor, and sleeping in the cold season with the windows open. Common hardening methods include baths, showers and other water procedures. For children, without restrictions, they can walk outdoors for at least four hours in appropriate clothing in any weather. Air baths with morning exercises for 10-15 minutes at a temperature of +18-20C, daytime sleep in the fresh air or a well-ventilated room at +14-15C. Washing with water at a temperature of +14-16C, at which the water temperature is gradually reduced. Contrast dousing of feet: for healthy children under three years old 38*-22*-38*-22*, over three years old – 38*-18*-38*-18*. Staying in the sun in the summer can be supplemented by walking barefoot.
What do you know about prevention?
There are three types of flu prevention. This is prevention with vaccines (specific), chemoprophylaxis (antiviral drugs), nonspecific (hygiene). Chemoprophylaxis are drugs used to prevent influenza. Currently, the use of chemotherapy is recommended only for emergency prevention in areas of influenza disease as prescribed by a doctor. Non-specific prevention: avoid contact with sick people, wear a medical mask when in contact with sick people, wash your hands often with soap, do not touch your eyes, nose and mouth with dirty hands, maintain personal hygiene, regularly ventilate the room, a balanced diet including enough vegetables and fruits , dress according to the season, observe the optimal work and rest schedule.
Myth four: there is no point in getting a flu shot; the child will still get sick.
M.P. The influenza virus is one of the most dangerous viruses that causes acute respiratory infections. The frequency of complications, including deaths, reaches up to 500 thousand children per year in the world. Almost every tenth child develops pneumonia. Vaccination is the main method of preventing influenza, while strong immunity is formed after four weeks and lasts six months, providing a protective effect of 70-90%. The strain of the virus changes every year, so it is necessary to get vaccinated annually. Vaccination does not provide a 100% guarantee that the child will not get sick, but after vaccination the disease will occur in a milder form, without complications.
Photo: courtesy of Dr.
Source: Zoya IGNATIEVA
If you notice a typo in the text, simply select this fragment and press Ctrl+Enter to inform the editor about it. Thank you!
2023-10-26 07:49:00
#Children #adults #colds #drafts