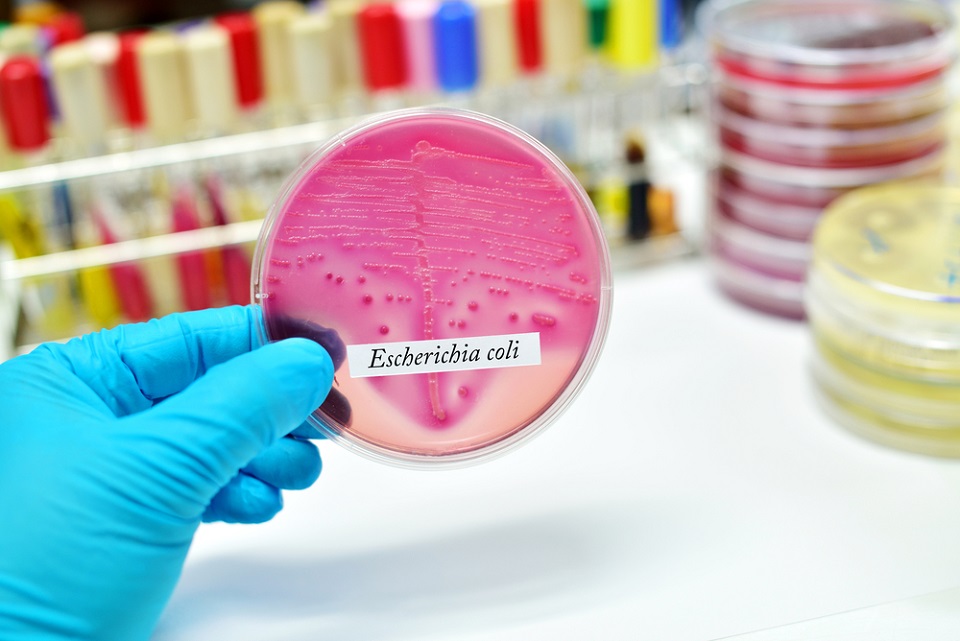
In the world of bacteria there are some microorganisms that can have a significant impact on human health. One of these is Escherichia coli (E. coli). We explain in this material what this bacterium is, how it is transmitted and how it affects the human body. You will also learn what the symptoms of E. coli infection are and when it is the right time to seek medical help. With this information, you will be able to better protect your health and prevent complications related to this bacteria.
What is Escherichia coli (E. Coli)?
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a type of bacteria that normally lives in the intestines of humans and animals. Most strains of E. coli are harmless and even beneficial, aiding digestion and absorption of nutrients needed by the body. However, there are also strains that can cause serious infections in the human body.
The impact of E. coli on the human body can be varied, depending on the strain of the bacteria and the individual’s immune system. Most E. coli infections cause mild symptoms that may appear a few days after exposure and usually last 5 to 7 days. In more serious cases, E. coli can cause urinary, respiratory or even blood infections. There are also strains of E. coli that can cause hemolytic uremic syndrome, a serious condition that can lead to kidney failure and even death.
It is important to note that although most E. coli infections can be successfully treated with adequate hydration and rest, there are cases where prompt medical intervention is necessary. (1)
Symptoms of E. Coli infection
Symptoms of E. Coli infection can range from mild to severe, depending on the strain of the bacteria and the degree of infection. The most common symptoms include:
diarrhea; stomach cramps; vomiting; fever.
Diarrhea can be watery or bloody, and abdominal cramps can be moderate or severe. Vomiting may occur in the first few days of infection, and fever may be present in association with the other symptoms.
In more severe cases, E. Coli infection can lead to complications such as hemolytic uremic syndrome, hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and acute renal failure.
The incubation time of E. Coli infection can vary, but symptoms usually appear 3-4 days after ingesting the bacteria. It is important to note that in some cases symptoms may appear earlier or later, depending on the strain of the bacteria and the body’s resistance to it. (1), (2)
Mode of transmission of E. Coli infection
E. coli bacteria is mainly transmitted by consuming contaminated food or water. The bacteria can be present in raw or undercooked meat, unpasteurized milk, unwashed fruits and vegetables, or water contaminated with feces. The consumption of these contaminated foods or liquids can lead to the infection of the human body with E. coli. It is important to pay attention to the hygiene of the food you eat and make sure it is properly prepared and comes from safe sources.
E. coli can also be passed from one person to another, especially with poor hygiene. Bacteria can be transferred from the hands to the mouth, causing the infection to spread. That’s why it’s essential to wash your hands with soap and warm water regularly, especially before preparing or eating food, after using the toilet, changing a baby’s diaper or caring for an elderly person. Avoiding contact with an infected person is essential, but when you have a child with this problem you need to take care of him and pay extra attention to hygiene.
The infection can also be transmitted through the contamination of kitchen utensils that are used without being cleaned and sanitized.
Animals, especially farm animals, can carry E. coli. People who come into contact with these animals or the environment in which they live can be exposed to infection. In other words, people who visit farms or work in the agricultural industry can be exposed to the bacteria.
Hospitals and all healthcare facilities are areas where infections can spread quickly, particularly through poor hand and surface hygiene.
To prevent the transmission of E. coli infection, it is recommended to follow strict hygiene rules in all aspects of daily life. (2)
When to go to the doctor?
Recognizing the symptoms is crucial when a person suspects an E. coli infection. To avoid complications, it is important to consult a doctor when symptoms such as:
severe diarrhea (often bloody); strong abdominal cramps; vomiting, which does not improve after a period of 5-7 days or which worsens; severe dehydration is a red flag, the problem requires immediate medical attention.
Awareness of the risk of complications is a crucial element also because there are categories of people more prone to this infection, for whom the state of health can worsen rapidly. People with weakened immune systems, young children, the elderly, and individuals with diagnosed chronic illnesses, such as kidney disease, are more prone to complications from E. coli infection. (1), (2)
Even in the presence of mild symptoms, it is important to consult the doctor for a correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment, thus preventing severe complications.
Information sources:
2. E. coli (Escherichia coli) –
2023-10-02 11:00:30
#Escherichia #coli #coli