Circuits in series and in parallel are two different things. Electric series and parallel also have quite significant circuit differences. Definitely a network electricity which often appear in physics have their respective uses.
In physics, there are two types of electrical circuits that you should understand. The two types are in series and in parallel.
This electrical circuit is certainly also useful for everyday life. By applying an electrical circuit, we can all enjoy the convenience of electronic products.
Read also: Intensity, definition, types and characteristics of the electric current
Information on series and parallel circuits
Surely you have noticed that the lights are on at home or on the street. Have you ever thought about how to turn on so many lights?
The answer is because there is an electrical circuit. However, electrical circuits fall into two distinct types, namely series and parallel circuits.
The difference between the two is also quite significant. Before discussing the two types further, it would be best if you knew what an electrical circuit is.
An electrical circuit is a path or circuit that works to cause electrons to flow from a source of electrical current or voltage.
This electron transfer process is known as electricity. The electrons will flow into the material that conducts the electric current, which is the conductor.
Why is it called a series circuit?
After knowing what the meaning of an electrical circuit is, then we can study the two types. There are two types of electrical circuits, namely in series and in parallel.
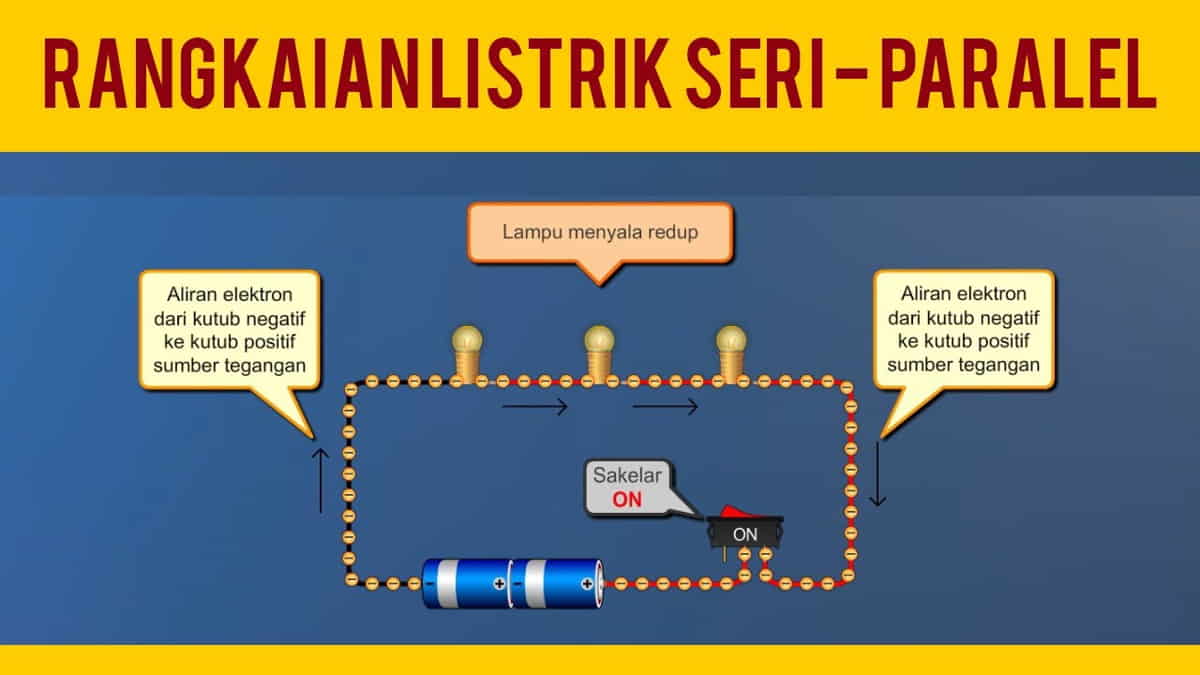
A series electrical circuit is an electrical circuit whose resistors are arranged next to each other or parallel. This is why the series of names.
The name of the series appears because the arrangement of the series is according to the series. Hence, there is only one path of electric current in this circuit.
The circuit will be installed in parallel and in sequence. Therefore, there is no current branching in this series electrical circuit.
Of course, the absence of branches in this electrical circuit also has a certain effect. Like when a component is damaged, for example.
If one of the components of a series electrical circuit is damaged, it will spread to all components. This happens because a series circuit has only one electrical path.
In the event of a disturbance, electricity will no longer be able to flow. This is the difference between series and parallel electrical circuits.
Read also: Examples of dynamic electricity easy to find in everyday life!
What is the parallel electrical circuit?
To understand what series and parallel circuits are, you also need to understand both. The meaning of parallel electricity is different from electric circuits in series.
If a series circuit has only one path with no branching, the parallel has branching currents. The very meaning of parallel electrical flow means that all components have the same source.
So there will be different paths of electric current paths. The branching of this electric current can be described by a circuit that has two resistors.
This parallel electrical circuit has several characteristics. One of its features is that it has a higher level of complexity than series circuits. This is the result of the arrangement of parallel electrical circuits.
The next feature is that each component will have the same voltage. However, the magnitude of each stream will vary in number due to the influence of the number of roads it can cross.
Read also: Kirchoff’s first and second law in electrical circuit systems, here is the definition!
What is the difference between series and parallel circuits?
After knowing the definition or understanding, the next step is to understand the difference between the two. The following is the difference between series and parallel electrical circuits.
- Components inside
The first difference is the components used by each circuit. Both series and parallel electricity have different arrangements.
Certainly the series components will be less. In a series circuit there are only sources of voltage, resistance and wires. Examples include cables, light bulbs, and switches.
While the parallel requires more components. Like more switches, longer tables and more.
- Form of network organization
The most obvious difference is the form of arrangement between the series and parallel circuits. A series circuit will only have one wire connecting the electrical resistor.
While the parallel has more than one current. Each wire will also have more than one connection, so there will be some resistance in the circuit.
Knowing the electrical circuits in series and in parallel is very useful because they are often applied in everyday life. Understanding this, it will avoid mistakes when installing electricity. (R10 / HR-Online)