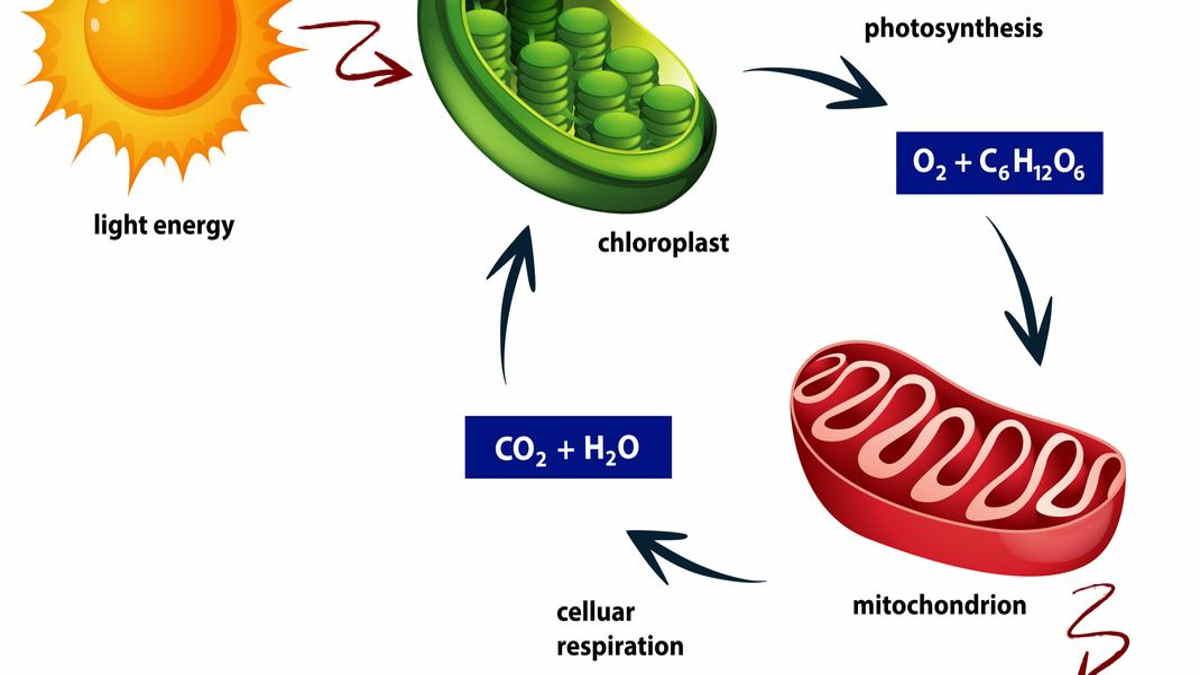
The definition of cellular respiration generally occurs in plants and animals. To do this they utilize the nutrients glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids.
Most of the energy flow through the biosphere begins with photosynthesizing organisms.
Then, some of this energy is obtained by organisms, including animals that will later eat the results of photosynthesis and other organisms.
Also Read: Vacuole Function in Plant Cells, Has a Very Important Role
What is Cell Respiration?
Respiration in cells has a meaning as the process of converting potential energy and nutrients into energy that the body or organism can use where the cell is located.
This process will occur in animals and plants. Cellular respiration will generally involve the oxidation of molecules to release energy, but respiration can also be accomplished without oxygen.
Cellular respiration occurs using organic molecules from food, such as fatty acids, sugars, and amino acids that can produce energy.
The energy will be stored in the organism in the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecule and also in heat.
Launching from the University of California, the process of cellular respiration will also produce carbon dioxide and water.
Cell respiration developed after the early photosynthetic bacteria began to provide a stable and abundant source of oxygen, after oxygen had accumulated in the atmosphere and the ocean.
Also Read: Differences in Animal and Plant Cells, Judging from the Presence of Organelles
Types of Cell Respiration
Cellular respiration is divided into two basic cellular respiration, namely aerobic and anaerobic.
Aerobic means with oxygen. In the aerobic process, oxygen functions to break down molecules and then releases adenosine triphosphate (ATP) which is energy.
While anaerobic respiration is much more efficient because it does not require oxygen. Anaerobic respiration can produce up to 30 ATP per nutrient molecule.
However, it requires a slower process to achieve. Since it does not require oxygen, fermentation is a form of anaerobic respiration.
Anaerobic respiration is also much faster than aerobic respiration. However, it is only able to produce two ATP from each molecule. As reported in AnaerobicRespiration.net, humans are able to use both terms of cellular respiration.
Purpose of Cell Respiration
Cellular respiration aims to produce energy in a form that organisms can later use.
Without respiration in the cells, any existing animal, plant, human or microorganism cannot survive because they do not get the energy they need.
Also Read: Cell Wall Function For Plant Survival
Factors Affecting Respiration
Here are some factors:
- Climatic conditions, such as ambient temperature and rainfall patterns that occur. Temperatures that are too high or low will affect breathing organisms.
- Species interactions, in this case, the main species interaction is how they eat each other’s food.
- The process of evolution, the evolution that occurs can change the rate of growth and reproduction of organisms.
- Abiotic environmental factors, factors that can influence the chemical reactions of respiration are nutrients, acidity of water, and availability of oxygen.
That is the process of understanding cellular respiration that occurs in organisms on Earth to survive. During respiration the product produced is ATP which is energy. (R10/HR-Online)
–