Particles that make up the Atom – Definition, History, Electrons, Protons, Neutrons, Atomic Nuclei, Experts: Atom is a basic unit of matter consisting of an atomic nucleus and a negatively charged electron cloud that surrounds it.
Understanding Atom
The first understanding of the atom was recorded from Greece by Leucippus and Democritus as early as 500 BC-400 BC, that every matter can be divided into smaller parts until the smallest indivisible part is obtained which is called atomos (atoms) and atoms are the smallest constituents. of all existing materials. In other words, an atom or atomos is the smallest particle that cannot be divided or split any further.
Also Read Articles That May Be Related: Definition and Kinds of Substance Classification
The second understanding of the atom by Aristotle in 384 BC and 332 BC, that matter can be divided continuously into smaller parts. It is clear that Aristotle’s views were different. We cannot use these two assumptions about atoms as a scientific basis because they are purely the result of thoughts and observations, not through experiments.
Understanding the atom by Joseph John Thompson, a physicist, that the atom is a sphere of positive charge and in it scattered electrons like raisins. The term “atom” was first used by the English chemist John Dalton (1766-1844) when he proposed his atomic theory in 1807.
Dalton said that all chemical elements are composed of very small particles, called atoms, which cannot be broken apart when chemical substances are reacted. Another opinion is that all chemical reactions are the result of joining or separating atoms. Dalton’s atomic theory became the basis for modern science.
The History of the Discovery of the Atom
The experimental history of the discovery of the atom began in 1803 by John Dalton, an English chemist who initiated the atomic theory. Then some supporting research on the discovery of atoms such as Michael Faraday in 1832 who discovered about electrolysis, namely breaking molecules using electricity.
Also Read Articles That May Be Related: Complete Definition and Types of Energy
Dmitri Mendeleev about his periodic law in 1869, then James Clerk Maxwell in 1873 who conducted experiments on electricity and electric fields (the existence of electrons), then in 1870 by Sir William Crookes who experimentally discovered that electrons have mass through cathode ray experiments that shot it.
Furthermore, E. Goldstein (1886) who discovered the existence of the constituent atoms of the positively charged proton. Then GJ Stoney (1894) officially named the negative particles that make up atoms that cause electricity as electrons.
Then after that JJ Thompson in 1897 discovered the mass of electrons using a cathode ray tube and in that year also discovered the existence of protons.
Furthermore, continued by his student, Rutherford, discovered about the radiation emitted by uranium and thorium, namely: alpha and betas. And draw the conclusion that there is an atomic nucleus in the atom. Rutherford also hypothesized that there was a nucleus other than protons that kept the atom in balance.
Rutherford’s hypothesis was later proven by James Chadwick in 1932. With the discovery of the neutrally charged neutron atomic particle. This is indeed quite difficult to find because it has a neutral charge. With the discovery of all the atomic particles, the real atomic model is complete.
Also Read Articles That May Be Related: 4 Understanding Atomic Structure And Its Model In An Expert Theory
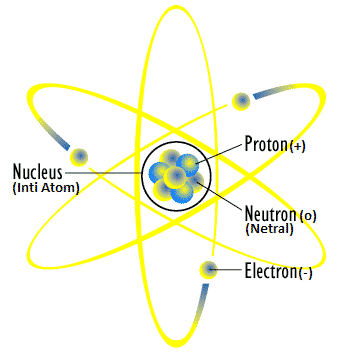
Atomic Composing Particles
X = Element
Z = Atomic number (in neutral atoms, electrons (e) = protons (p)
A = Mass number = number of protons + neutrons
The basic particles that make up an atom are protons, neutrons and electrons. Here’s what it means:
Neutrons have no charge or are neutral and in 1932, were discovered by the British physicist James Chadwick.
Protons have a positive charge and were discovered by Goldstein in 1886.
Electrons have a negative charge and were discovered by JJ. Thompson in 1897.
Electron
In this case do you pay attention to the television tube?? television tube is a cathode ray tube, which in the cathode ray tube experiment was first carried out.
The result of his experiment was the discovery of a beam of light that appeared from the cathode to the anode, which was called cathode rays. George Johnstone Stoney “1891” who gave the name cathode rays are called “electrons”.
The weakness of Stoney is not being able to explain the meaning of atoms in an element having the same properties while different elements will have different properties, even though they both have electrons.
Atoine Henri Becquerel “1896” determined the rays emitted from radioactive elements which have properties similar to electrons. And Joseph John Thomson “1897” continued the experiment of William Crookes, namely the influence of electric and magnetic fields in a cathode ray tube.
Which in this case the results of his experiments proved that there are negatively charged particles in an atom because the rays can be allowed to move towards the positive pole of the electric field.
The magnitude of the charge in electrons was discovered by Robert Andrew Milikan “1908”, oil is sprayed into an electrically charged tube, due to the gravitational attraction it will precipitate the falling oil droplets.
If the oil droplets are given a negative charge then they will be attracted to the positive polarity of the electric field. The results of Milikan and Thomson’s experiment obtained an electron-1 charge and an electron mass of 0, so that the electron can be denoted “0e-1”.
Also Read Articles That May Be Related: Explanation of Reptile Characteristics in Biology
History of the Discovery of Electrons by Experts
Electrons are not simply discovered. There are several scientists whose work became pioneers in the discovery of electrons. Here are four scientists who played a phenomenal role in laying the groundwork for the discovery of the electron.
-
Johann Wilhelm Hittorf
In 1869, a German physicist, John Wilhelm Hittorf through his research on the electrical conductivity in gas cylinders found that the intensity of light emitted from the cathode plate depends on the gas pressure.
-
Eugen Goldstein
In 1876, this German physicist discovered that the rays emitted from light in an earlier experiment by John Wilhelm cast a shadow when an object was placed behind it. He named these rays as cathode rays.
-
William Crookes
In the 1870s, British physicist and chemist William Crookes built the first cathode ray tube which sparked the development of the theory of the existence of negatively charged particles in light that was bent from the anode to the cathode.
-
Arthur Schuster
The German-born British physicist continued Crooke’s work and became increasingly convinced that cathode rays had negatively charged particles.
-
Sir J. J Thompson: The Scientist Behind the Discovery of the Electron
In 1896, British physicist JJ Thompson and his colleagues named John S. Townsend and HA Wilson conducted several experiments and conclusively proved the existence of electrons.
So, it can be concluded that JJ Thompson was the one who discovered the electron. Through experiments using cathode ray tubes, Thompson determined that cathode rays were particles unlike waves, atoms, or molecules.
He also managed to calculate the approximate value of the ratio between e (electric charge) and (m) mass. But JJ Thompson has not been able to calculate the value of the charge and mass of electrons independently.
Robert Millikan is the person who managed to calculate the charge and mass of electrons independently in 1909. Electrons have a negative charge of -1.6 x 10-19 Coulomb and its mass is 9.1 x 10-31 kg. For his valuable contributions to the discovery of the electron and to his work on the conduction of gases, Sir J. J Thompson was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1896.
Proton
If the electron mass is 0, it means that a particle has no mass, whereas matter particles have a measurable mass. Similarly, the fact that the atom is neutral, how can the atom be neutral and have, if there are only electrons in the atom ..?? Eugene Goldstein “1886” conducted an experiment from a gas cylinder which had a cathode, which was perforated and given an electric charge.
Also Read Articles That May Be Related: Definition, Characteristics and Classification of Aves (Birds) along with the most complete examples
You are an Atom
After the discovery of the proton and electron, Ernest Rutherford carried out research into the thin plate bombardment. If the atom consists of particles that are positively and negatively charged, the alpha rays that are fired should not be passed through / through the plate so that the term atomic nucleus appears.
Ernest Rutherford assisted by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden “1911” discovered the concept of the atomic nucleus supported by the discovery of X-rays by Wc. X-ray “1895” and the discovery of Radioactive substances “1896”.
Neutron
Rutherford’s prediction spurred W. Bothe and H. Becker “1930” to experiment with shooting alpha particles at the nucleus of the beryllium “Be” atom, which resulted in high penetrating particle radiation.
This experiment was continued by James Chadwick “1932”, it turns out that the particles that cause high penetrating radiation are neutral or uncharged and have almost the same mass as protons, these particles are called neutrons and are denoted by.
Also Read Articles That May Be Related: Understanding Atoms and Atomic Theory According to Complete Experts
Maybe below is what you are looking for
–

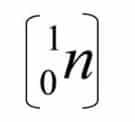

:quality(80)/cdn-kiosk-api.telegraaf.nl/13b2ddf4-1406-11ec-af08-0218eaf05005.jpg)