Jakarta: NASA’s Osiris-REX spacecraft will reportedly begin a return journey to Earth in the near future. The plane in charge of taking rock samples from the asteroid Bennu will travel to Earth for 2 years.
Quoting The Verge, this information is known from the Osiris-REX maneuver which fires a booster to return to Earth. This maneuver reportedly propels the spacecraft back into its winding cosmic path around the Sun and then into Earth’s orbit.
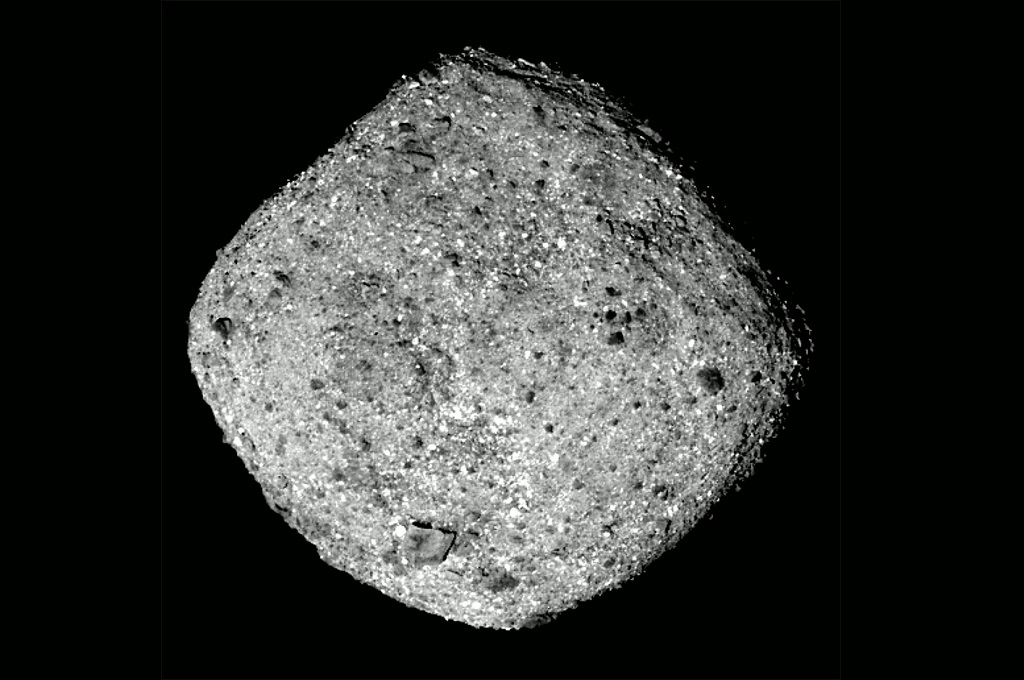
Osiris-REX is expected to arrive on Earth in 2023, and throw a capsule containing a sample of the asteroid Bennu through the atmosphere. This capsule is predicted to fall at a location in Utah, United States.
How do you feel about this article?
–
–
Meanwhile, the departure maneuver or what is known as the Asteroid Departure Maneuver (ADM) of the spacecraft is considered not difficult for the Osiris-REX team. But this marks a significant rarity leading to the return of the first pure asteroid sapel in NASA history.
Space aircraft technicians at Lockheed Martin, in Littleton, Colorado, United States confirmed that the booster fire maneuver which lasted for seven minutes occurred on Monday at 4:00 p.m. local time, and was celebrated by the technician.
As a reminder, the Osiris-REX was launched in Florida in 2016 and carries on a mission to travel more than 100 million miles to the asteroid Bennu. This asteroid takes its name from the Egyptian mythological god who was able to create the world.
Scientists hope that Benny is an ancient relic of an asteroid from the early period of the solar system and holds clues to the origin of life on Earth. In 2020, the Osiris-REX entered Bennu’s orbit and became the first US spacecraft to orbit the asteroid.
The craft then gradually approaches the surface of the extraterrestrial rock and extends its robotic arm with a collector-shaped device to a fountain at the end measuring 11 feet.
The collector’s head then takes samples from Bennu’s surface by releasing a burst of gas that is pressurized strong enough to kick up the rock and debris of the asteroid, and catch it in a container attached to the sampling head.
Bennu’s surface is said to be very soft and this maneuver caused more flying rocks than scientists predicted. The head collector reportedly managed to retrieve about 2 ounces of rock samples from the asteroid.
The rock samples were then put into a capsule on the plane, but Osiris-REX remained around Bennu for several months so that the dust covered the fuselage so that it could detonate it, in order to study the craters it had left on the asteroid’s surface.
After arriving in Utah, NASA will move the capsule and its contents to the Johnson Space Center in Houston. Researchers reportedly plan to study only 25 percent of the sample, and will retain the remaining 75 percent so that other scientists can study it in the future.
(MMI)
– .