–
It is reported on the 10th that Intel, a semiconductor company in the United States, is pushing ahead with a plan to entrust some of its chip production to foundries (consigned semiconductor production) companies such as Samsung Electronics and Taiwan TSMC. It is analyzed by the influence of criticism in the market that “Intel’s semiconductor production technology is not the same as before.”
Bloomberg News reported on the 9th (local time) that “Intel is in discussions with Samsung Electronics and TSMC on outsourcing some chip production.” The outsourced chips are expected to be fully produced in 2023. It is reported that Intel will decide whether to outsource production before the fourth quarter of last year’s earnings announcement on the 21st.
Intel is a’Integrated Semiconductor Company (IDM)’ that designs, manufactures and sells its own chips. Since there is a factory, there is no need to entrust production to companies such as TSMC and Samsung Electronics’ Foundry Division. It is known that Intel has seldom used outsourcing production for over 50 years of history.
The recent talk of’production outsourcing’ is due to the criticism that “semiconductor production technology is inferior to Samsung Electronics and TSMC.” Intel is mass-producing products in the process of 10 nanometers (nm, 1 nm = 1 billionth of a meter) circuit line width (the width of the transistor gate through which electrons flow). The narrower the line width, the smaller and more efficient high-performance semiconductors can be made.
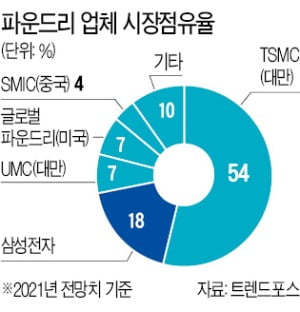
Samsung Electronics’ foundry division and TSMC currently produce chips by receiving orders from customers in ultra-fine processes with a line width of 7 nm and 5 nm. Intel’s central processing unit (CPU) rival AMD is a major customer of TSMC’s 7nm process. For this reason, from the beginning of last year, the evaluation that “AMD CPU from 7nm process is better than Intel’s 10nm product” was dominant. At the end of last year, a hedge fund that owned a 0.5% stake in Intel publicly criticized Intel’s technology.
As this situation continued, there was a story inside Intel that’some semiconductor production can be left to a foundry.’ In July and October of last year, Intel CEO Robert Swan said, “From 2023, we can supply products through Intel’s 7nm process,’external process’ or’combination of the two processes’.”
In the semiconductor industry, it is highly likely that Taiwanese TSMC will take Intel’s supply. Bloomberg said, “TSMC is preparing 4nm and 5nm lines to win orders for Intel,” and said, “Consultation with Samsung Electronics is in an early stage compared to TSMC.” However, some observers say that Samsung Electronics will “reverse” or share Intel supplies with technology and price, just as Samsung Electronics won an order for Qualcomm’s latest smartphone application processor (AP)’Snapdragon 888′ last year.
Some analysts say that even if the order volume goes to either TSMC or Samsung Electronics, it is not a’hit’. This is because the foundry’s production capacity is not meeting demand. An industry expert said, “There are only two places in the world that can handle ultra-fine processes under 10 nm, Samsung Electronics and TSMC.” “We have no choice but to go to Samsung Electronics,” he said.
Reporter Hwang Jeong-soo [email protected]
–
Ⓒ Hankyung.com prohibits unauthorized reproduction and redistribution
–