–
(Seoul = Yonhap News) Reporter Lee Ji-eun = Dealing room at Hana Bank headquarters in Jung-gu, Seoul on the afternoon of February 18. On this day, KOSPI closed at 3,086.66, 47.07 points (1.50%) down from the previous day. [email protected]
–
The overall environment of the stock market in 2021 is expected to be significantly different from that of 2020. In 2020, despite the widespread pessimism about the real economy due to the spread of Corona 19, Korea and other global stock markets rose significantly thanks to the central bank’s expanding monetary policy and the government’s active economic stimulus measures.
Above all, the power of low interest rates was great. The economy ended up avoiding a sudden fall with the power of policy, but the stock market was able to boom with the power of liquidity released by the central bank. The dramatic enthusiasm for individual investors in Korea can also be interpreted as a result of investors who could not withstand low interest rates and chose risky assets.
2021 is expected to be the exact opposite of 2020. The economy is likely to improve significantly. There is high hope that the Corona 19 vaccine will become a game changer. Corona 19 will remain in everyday life for a long time in the future, but it is unlikely that at least a cessation of economic activities such as 2020 will be repeated.
The number of confirmed cases in major countries is already declining significantly. Korea’s GDP (gross domestic product) growth rate is expected to reverse from -1% last year to around 2.5% this year, and the US is also expected to rebound from -3.5% to 4.1%. do.
Interest this year is the movement of interest rates. It is highly likely that the economy will improve, and interest rates are expected to rise as well. The economic upturn is good for the stock market, but rising interest rates are likely to act as bad news.
In particular, since Korea and other global stock markets have risen without any adjustment since March last year, rising interest rates could be an opportunity to adjust. US interest rates, which act as the rudder of global interest rates, are already rising rapidly.
Increasing interest rates does not mean that the stock price will turn downward. This is because, as discussed earlier, rising interest rates are a shadow of economic recovery. In the initial phase of rising interest rates, the stock market reflects the economic upturn in the stock price. So, a process of rising interest rates and stock prices appears.
However, if the interest rate rises above a certain level, the negative factor of the higher interest rate becomes more influential than the positive factor of an economic recovery. How far will the replacement interest rate rise before the stock market will be affected?
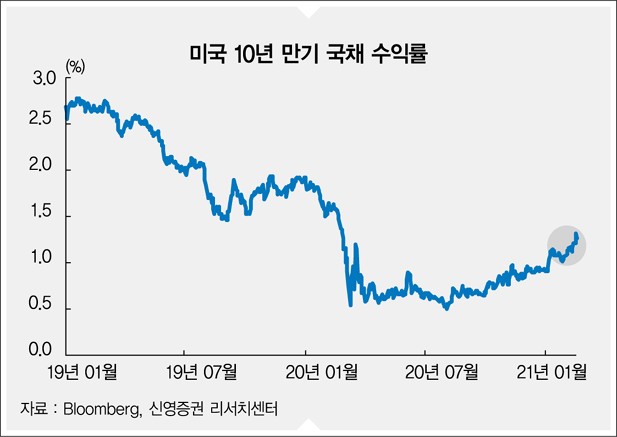
Although the interaction between interest rates and stock prices cannot be replaced with a declining causal relationship, it is likely that around 1.5% of the US 10-year Treasury bond yield will be an inflection point. 1.5% is the level of the US interest rate before the Corona 19 pandemic, and it is also a level that exceeds the dividend yield of 1.47% (as of February 17) for the stocks in the US S&P500.
In addition, the rise in nominal interest rates raises expectations that the central bank will eventually tighten. It is very unlikely that the US Federal Reserve, which has promised to maintain a low interest rate stance, will use a tightening policy right away this year, but it is easy to spread the perception that once it enters the tightening cycle, the rate of rate hikes could be steep.
As the market always advances expectations and reflects it in the stock price, concerns that the pace of tightening can be strengthened at any time will be a negative factor for the stock market. As of Feb. 17, the US 10-year Treasury bond yield is at 1.27%.
–
[신영증권 제공]
–
If the interest rate rises further from the current level, it is highly likely to act as an excuse for correction in the stock market, which has been running unwaveringly. However, rather than turning to a structural bear market, it will only be a temporary adjustment.
This is because if interest rates soar to the extent that the level itself varies, the real economy may suffer a big blow, not a problem in terms of stock market adjustment. Then the central bank will come out again. Just as the U.S. Federal Reserve in 2019 lowered interest rates in the name of’insurance’.
Since there is no room to lower the policy rate anymore, it will be in the form of a commitment to suppress long-term rate hikes by expanding quantitative easing or to keep policy rates low over the long term.
The key to responding to the stock market in 2021 is to prepare for any adjustments that may occur in the face of rising interest rates. Strategic reduction of the stock weighting is not desirable, as it is highly likely to only be temporarily adjusted. In the corona 19 pandemic phase, it is necessary to consider fine adjustments to a certain extent to increase the proportion of cash in consideration of the intensity and valuation of the stock price.
It is also necessary to build a portfolio with stocks that can withstand rising interest rates relatively well. Since rising interest rates are basically the product of an economic recovery, it is necessary to pay attention to the stocks whose profits are increasing in this economic expansion phase.
On the other hand, it is worth considering that stocks armed with growth values that are difficult to measure when interest rates go up. Although the meaning of the inertial distinction between growth stocks and value stocks has weakened, there is a high possibility that stocks belonging to the traditional industry will be relatively good.

–
[김학균 제공]
–
<저작권자(c) 연합뉴스,
Unauthorized reproduction-redistribution prohibited>
2021/02/27 10:30 sent
–
![[마이더스] Interest rates on the stock market in 2021 [마이더스] Interest rates on the stock market in 2021](https://img1.yna.co.kr/photo/yna/YH/2021/02/18/PYH2021021818610001300_P4.jpg)

